One of the most common questions I have been asked over the last 8 years is whether or not we are submitting OpenAPS to the FDA for regulatory approval.
This question is a big red herring.
Regulatory approval is often seen and discussed as the one path for authenticating and validating safety and efficacy.
It’s not the only way.
It’s only one way.
—
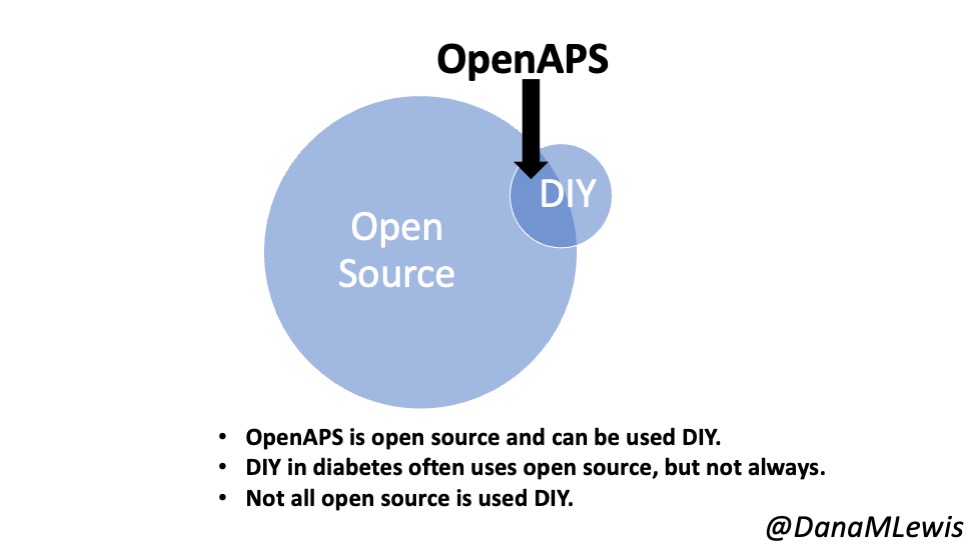
As background, you need to understand what OpenAPS is. We took an already-approved insulin pump that I already had, a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) that I already had, and found a way to read data from those devices and also to use the already-built commands in the pump to send back instructions to automate insulin delivery via the decision-making algorithm that we created. The OpenAPS algorithm was the core innovation, along with the realization that this already-approved pump had those capabilities built in. We used various off the shelf hardware (mini-computers and radio communication boards) to interoperate with my already approved medical devices. There was novelty in how we put all the pieces together, though the innovation was the algorithm itself.
The caveat, though, is that although the pump I was using was regulatory-approved and on the market, which is how I already had it, it had later been recalled after researchers, the manufacturer, and the FDA realized that you could use the already-built commands in the pump’s infrastructure. So these pumps, while not causing harm to anyone and no cases of harm have ever been recorded, were no longer being sold. It wasn’t a big deal to the company; it was a voluntary recall, and people like me often chose to keep our pumps if we were not concerned about this potential risk.
We had figured out how to interoperate with these other devices. We could have taken our system to the FDA. But because we were using already-off-the-market pumps, there was no way the FDA would approve it. And at the time (circa 2014), there was no vision or pathway for interoperable devices, so they didn’t have the infrastructure to approve “just” an automated insulin delivery algorithm. (That changed many years later and they now have infrastructure for reviewing interoperable pumps, CGM, and algorithms which they call controllers).
The other relevant fact is that the FDA has jurisdiction based on the commerce clause in the US Constitution: Congress used its authority to authorize the FDA to regulate interstate commerce in food, drugs, and medical devices. So if you’re intending to be a commercial entity and sell products, you must submit for regulatory approval.
But if you’re not going to sell products…
This is the other aspect that many people don’t seem to understand. All roads do not lead to regulatory approval because not everyone wants to create a company and spend 5+ years dedicating all their time to it. That’s what we would have had to do in order to have a company to try to pursue regulatory approval.
And the key point is: given such a strict regulatory environment, we (speaking for Dana and Scott) did not want to commercialize anything. Therefore there was no point in submitting for regulatory approval. Regardless of whether or not the FDA was likely to approve given the situation at the time, we did not want to create a company, spend years of our life dealing with regulatory and compliance issues full time, and maybe eventually get permission to sell a thing (that we didn’t care about selling).
The aspect of regulatory approval is a red herring in the story of the understanding of OpenAPS and the impact it is having and could have.
Yes, we could have created a company. But then we would not have been able to spend the thousands of hours that we spent improving the system we made open source and helping thousands of individuals who were able to use the algorithm and subsequent systems with a variety of pumps, CGMs, and mobile devices as an open source automated insulin delivery system. We intentionally chose this path to not commercialize and thus not to pursue regulatory approval.
—
As a result of our work (and others from the community), the ecosystem has now changed.
Time has also passed: it’s been 8 years since I first automated insulin delivery for myself!
The commercial players have brought multiple commercial AIDs to market now, too.
We created OpenAPS when there was NO commercial option at the time. Now there are a few commercial options.
But it is also an important note that I, and many thousands of other people, are still choosing to use open source AID systems.
Why?
This is another aspect of the red herring of regulatory approval.
Just because something is approved does not mean it’s available to order.
If it’s available to order (and not all countries have approved AID systems!), it doesn’t mean it’s accessible or affordable.
Insurance companies are still fighting against covering pumps and CGMs as standalone devices. New commercial AID systems are even more expensive, and the insurance companies are fighting against coverage for them, too. So just because someone wants an AID and has one approved in their country doesn’t mean that they will be able to access and/or afford it. Many people with diabetes struggle with the cost of insulin, or the cost of CGM and/or their insulin pump.
Sometimes providers refuse to prescribe devices, based on preconceived notions (and biases) about who might do “well” with new therapies based on past outcomes with different therapies.
For some, open source AID is still the most accessible and affordable option.
And in some places, it is still the ONLY option available to automate insulin delivery.
(And in most places, open source AID is still the most advanced, flexible, and customizable option.)
—
Understanding the many reasons why someone might choose to use open source automated insulin delivery folds back into the understanding of how someone chooses to use open source automated insulin delivery.
It is tied to the understanding that manual insulin delivery – where someone makes all the decisions themselves and injects or presses buttons manually to deliver insulin – is inherently risky.
Automated insulin delivery reduces risk compared to manual insulin delivery. While some new risk is introduced (as is true of any additional devices), the net risk reduction overall is significantly large compared to manual insulin delivery.
This net risk reduction is important to contextualize.
Without automated insulin delivery, people overdose or underdose on insulin multiple times a day, causing adverse effects and bad outcomes and decreasing their quality of life. Even when they’re doing everything right, this is inevitable because the timing of insulin is so challenging to manage alongside dozens of other variables that at every decision point play a role in influencing the glucose outcomes.
With open source automated insulin delivery, it is not a single point-in-time decision to use the system.
Every moment, every day, people are actively choosing to use their open source automated insulin delivery system because it is better than the alternative of managing diabetes manually without automated insulin delivery.
It is a conscious choice that people make every single day. They could otherwise choose to not use the automated components and “fall back” to manual diabetes care at any moment of the day or night if they so choose. But most don’t, because it is safer and the outcomes are better with automated insulin delivery.
Each individual’s actions to use open source AID on an ongoing basis are data points on the increased safety and efficacy.
—
However, this paradigm of patient-generated data and patient choice as data contributing toward safety and efficacy is new. There are not many, if any, other examples of patient-developed technology that does not go down the commercial path, so there are not a lot of comparisons for open source AID systems.
As a result, when there were questions about the safety and efficacy of the system (e.g., “how do you know it works for someone else other than you, Dana?”), we began to research as a community to address the questions. We published data at the world’s biggest scientific conference and were peer-reviewed by scientists and accepted to present a poster. We did so. We were cited in a piece in Nature as a result. We then were invited to submit a letter to the editor of a traditional diabetes journal to summarize our findings; we did so and were published.
I then waited for the rest of the research community to pick up this lead and build on the work…but they didn’t. I picked it up again and began facilitating research directly with the community, coordinating efforts to make anonymized pools of data for individuals with open source AID to submit their data to and for years have facilitated access to dozens of researchers to use this data for additional research. This has led to dozens of publications further documenting the efficacy of these solutions.
Yet still, there was concern around safety because the healthcare world didn’t know how to assess these patient-generated data points of choice to use this system because it was better than the alternative every single day.
So finally, as a direct result of presenting this community-based research again at the world’s largest diabetes scientific conference, we were able to collaborate and design a grant proposal that received grant funding from New Zealand’s Health Research Council (the equivalent of the NIH in the US) for a randomized control trial of the OpenAPS algorithm in an open source AID system.
An RCT is often seen as the gold standard in science, so the fact that we received funding for such a study alone was a big milestone.
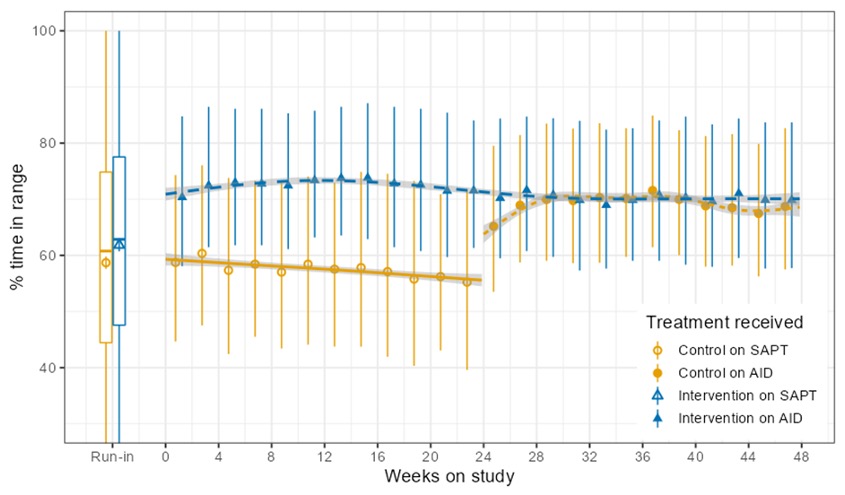
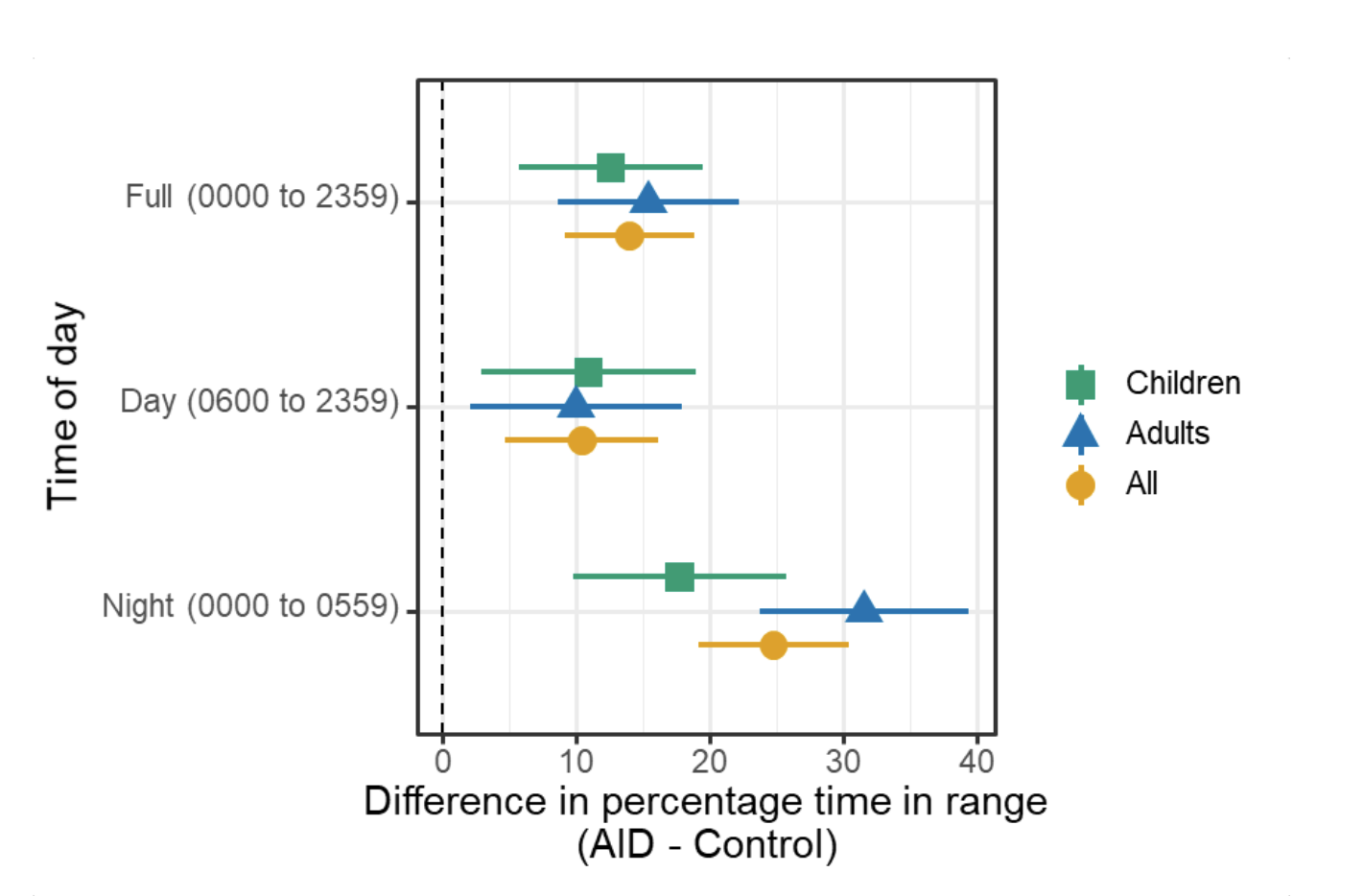
And this year, in 2022, the RCT was completed and our findings were published in one of the world’s largest medical journals, the New England Journal of Medicine, establishing that the use of the OpenAPS algorithm in an open source AID was found to be safe and effective in children and adults.
No surprises here, though. I’ve been using this system for more than 8 years, and seeing thousands of others choose the OpenAPS algorithm on an ongoing, daily basis for similar reasons.
—
So today, it is possible that someone could take an open source AID system using the OpenAPS algorithm to the FDA for regulatory approval. It won’t likely be me, though.
Why not? The same reasons apply from 8 years ago: I am not a company, I don’t want to create a company to be able to sell things to end users. The path to regulatory approval primarily matters for those who want to sell commercial products to end users.
Also, regulatory approval (if someone got the OpenAPS algorithm in an open source AID or a different algorithm in an open source AID) does not mean it will be commercially available, even if it will be approved.
It requires a company that has pumps and CGMs it can sell alongside the AID system OR commercial partnerships ready to go that are able to sell all of the interoperable, approved components to interoperate with the AID system.
So regulatory approval of an AID system (algorithm/mobile controller design) without a commercial partnership plan ready to go is not very meaningful to people with diabetes in and of itself. It sounds cool, but will it actually do anything? In and of itself, no.
Thus, the red herring.
Might it be meaningful eventually? Yes, possibly, especially if we collectively have insurers to get over themselves and provide coverage for AID systems given that AID systems all massively improve short-term and long-term outcomes for people with diabetes.
But as I said earlier, regulatory approval does necessitate access nor affordability, so an approved system that’s not available and affordable to people is not a system that can be used by many.
We have a long way to go before commercial AID systems are widely accessible and affordable, let alone available in every single country for people with diabetes worldwide.
Therefore, regulatory approval is only one piece of this puzzle.
And it is not the only way to assess safety and efficacy.
—
The bigger picture this has shown me over the years is that while systems are created to reduce harm toward people – and this is valid and good – there have been tendencies to convert to the assumption that therefore the systems are the only way to achieve the goal of harm reduction or to assess safety and efficacy.
They aren’t the only way.
As explained above, FDA approval is one method of creating a rubber stamp as a shorthand for “is this considered to be safe and effective”.
That’s also legally necessary for companies to use if they want to sell products. For situations that aren’t selling products, it’s not the only way to assess safety and efficacy, which we have shown with OpenAPS.
With open source automated insulin delivery systems, individuals have access to every line of code and can test and choose for themselves, not just once, but every single day, whether they consider it to be safer and more effective for them than manual insulin dosing. Instead of blindly trusting a company, they get the choice to evaluate what they’re using in a different way – if they so choose.
—
So any questions around seeking regulatory approval are red herrings.
A different question might be: What’s the future of the OpenAPS algorithm?
The answer is written in our OpenAPS plain language reference design that we posted in February of 2015. We detailed our vision for individuals like us, researchers, and companies to be able to use it in the future.
And that’s how it’s being used today, by 1) people like me; and 2) in research, to improve what we can learn about diabetes itself and improve AID; and 3) by companies, one of whom has already incorporated parts of our safety design as part of a safety layer in their ML-based AID system and has CE mark approval and is being sold and used by thousands of people in Europe.
It’s possible that someone will take it for regulatory approval; but that’s not necessary for the thousands of people already using it. That may or may not make it more available for thousands more (see earlier caveats about needing commercial partnerships to be able to interoperate with pumps and CGMs).
And regardless, it is still being used to change the world for thousands of people and help us learn and understand new things about the physiology of diabetes because of the way it was designed.
That’s how it’s been used and that’s the future of how it will continue to be used.
No rubber stamps required.



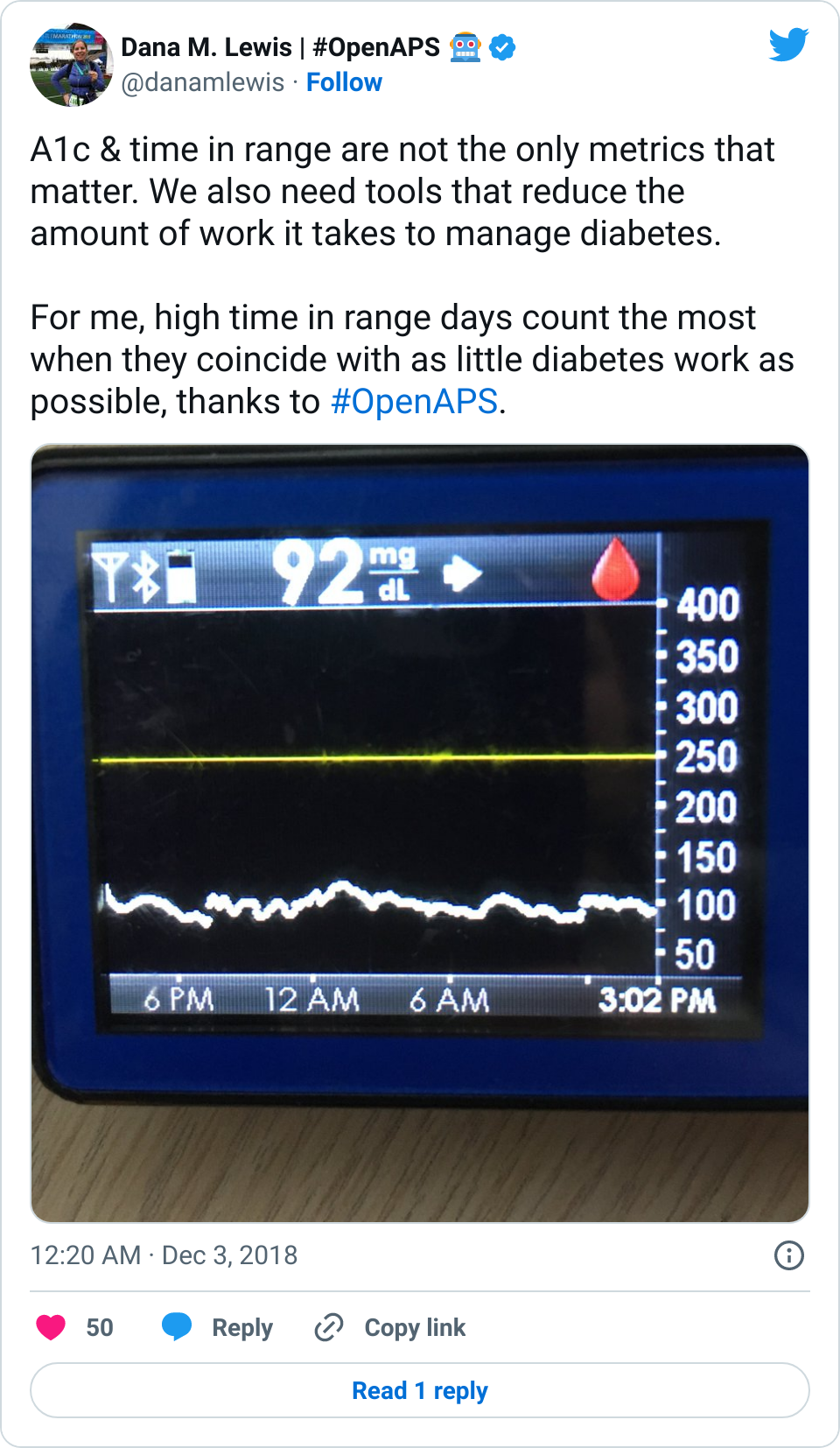
 If it’s a fellow person with diabetes or a loved one, we talk about what problems they might be having or what areas they’d like to improve or what behaviors they’d like to change, if any. That’s usually way more effective than hearing “X.x%” of an A1c, and them wondering silently how to get there or what to do differently if someone wants to change things. (Or for clinicians who ask me, it turns into a discussion about choices and behaviors and tradeoffs that patients may choose to make.)
If it’s a fellow person with diabetes or a loved one, we talk about what problems they might be having or what areas they’d like to improve or what behaviors they’d like to change, if any. That’s usually way more effective than hearing “X.x%” of an A1c, and them wondering silently how to get there or what to do differently if someone wants to change things. (Or for clinicians who ask me, it turns into a discussion about choices and behaviors and tradeoffs that patients may choose to make.)











Recent Comments