I have a new part-time job as a pancreas, but this time, I don’t have any robot parts I can make to help.
This is a joke, because I have had type 1 diabetes for 19+ years and 7 years ago I helped make the world’s first open-source artificial pancreas, also known as an automated insulin delivery system, that we jokingly call my “robot parts” and takes care of 90+% of the work of living with type 1 diabetes. PS if you’re looking for more information, there’s a book for that, or a free 3 minute animated video explaining automated insulin delivery.
The TL;DR of this post is that I have discovered I have a mild or moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, known as EPI (or PEI, pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, depending on which order and acronym you like). There’s a treatment called pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) which I have been trying.
It took a long time for me to get diagnosed (almost 2 years), so this post walks through my history and testing process with my gastroenterologist (GI doctor) and the importance of knowing your own body and advocating for yourself when something is wrong or not quite right.
Background
About six years after I was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, I was doing a summer internship in Washington, D.C. (away from home) and started getting chest tightness and frequent abdominal pain. Sometimes it felt like my abdominal muscles were “knitting” into each other. Because I had type 1 diabetes, I had heard at one point that about 10% of people with type 1 also develop celiac disease. So, thankfully, it was as simple as calling my endocrinologist and scheduling testing, and getting an endoscopy and biopsy to confirm I had celiac disease. It took about 2 months, and the timing was mostly that long due to getting back to Alabama after my internship and the testing schedule of the hospital. This is relevant detail, because I later read that it takes an average of 7 years for most people to get diagnosed with celiac disease. That has been floating around in my brain now for over a decade, this awareness that GI stuff is notoriously hard to diagnose when you’re not lucky enough to have a clear idea, like I did, of an associated condition.
So, with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease, I use automated insulin delivery to get great outcomes for my diabetes and a 100% very careful gluten-free diet to manage my celiac disease, and have not had any GI problems ever since I went gluten-free.
Until January/February 2020, when I took an antibiotic (necessary for an infection I had) and started to get very minor GI side effects on day 5 of the 7-day antibiotic course. Because this antibiotic came with a huge warning about C. diff, and I really didn’t want C. diff, I discontinued the antibiotic. My infection healed successfully, but the disruption to my GI system continued. It wasn’t C. diff and didn’t match any of the C. diff symptoms, but I really lost my appetite for a month and didn’t want to eat, so I lost 10 pounds in February 2020. On the one hand, I could afford to lose the weight, but it wasn’t healthy because all I could bring myself to eat was one yogurt a day. I eventually decided to try eating some pecans to add fiber to my diet, and that fiber and change in diet helped me get back to eating more in March 2020, although I generally was eating pecans and dried cranberries (to increase my fiber intake) for breakfast and wasn’t hungry until late afternoon or early evening for another meal. So, since my body didn’t seem to want anything else, I essentially was eating two meals a day. My GI symptoms were better: not back to how they were before February 2020, but seemed manageable.
However, in July 2020, one night I woke up with incredibly painful stabbing abdominal pain and thought I would need to go to the ER. Thankfully, it resolved enough within minutes for me to go back to sleep, but that was scary. I decided to schedule an appointment with my gastroenterologist. I took in a record of my symptoms and timing and explained what was most worrisome to me (sudden stabbing pains after I ate or overnight, not seemingly associated with one particular type of food; changes in bathroom habits, like steatorrhea, but not as severe as diarrhea). He made a list of suspected things and we began testing: we checked for C. diff (nope), parasites (nope), bloodwork for inflammation (nope, so no Crohn’s or IBS or IBD), my celiac markers to make sure I wasn’t being accidentally glutened (nope: 100% gluten-free as proven by the blood work), H. pylori (nope), and did a CT scan to check for structural abnormalities (all good, again no signs of inflammation or any obvious issues).
Because all of this happened during the global COVID-19 pandemic, I was cautious about scheduling any in-person tests such as the CT scan or the last test on my list, a colonoscopy and endoscopy. I have a double family history of colon cancer, so although it was extremely unlikely, given everything else on the list was coming back as negative, it needed to be done. I waited until I was fully vaccinated (e.g. 2 weeks after 2 shots completed) to have my colonoscopy and endoscopy scheduled. The endoscopy was to check for celiac-related damage in my small intestine since I hadn’t had an endoscopy since my diagnosis with celiac over a decade ago. Thankfully, there’s no damage from celiac (I wasn’t expecting there to be any damage, but is a nice confirmation of my 100% very careful gluten free diet!), and the colonoscopy also came back clear.
Which was good, but also bad, because…SOMETHING was causing all of my symptoms and we still didn’t know what that was. The last thing on my doctor’s list was potentially small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), but the testing is notoriously non-specific, and he left it up to me as to whether I decided to treat it or not. Having run out of things to test, I decided to do a two-week course of an antibiotic to target the bacteria. It helped for about two weeks, and then my symptoms came back with a vengeance. However, I had realized in spring 2021 (after about 9 months of feeling bad) that sometimes the stabbing abdominal pain happened when I ate things with obvious onion or garlic ingredients, so January-July 2021 I had avoided onion and garlic and saw a tiny bit of improvement (but nowhere near my old normal). Because of my research on onion and garlic intolerances, and then additional research looking into GI things, I realized that the low FODMAP diet which is typically prescribed for IBS/IBD (which I don’t have) could be something I could try without a lot of risk: if it helped, that would be an improvement, regardless of whatever I actually had.
So in August 2021, as noted in this blog post, I began the low FODMAP diet first starting with a careful elimination phase followed by testing and adding foods back into my diet. It helped, but over time I’ve realized that I still get symptoms (such as extreme quantities of gas, abdominal discomfort and distention, changed bathroom habits) even when I’m eating low FODMAP. It’s possible low FODMAP itself helped by avoiding certain types of food, but it’s also possible that it was helping because I was being so careful about the portions and timing of when I was eating, to avoid “stacking” FODMAPs.
One other thing I had tried, as I realized my onion and garlic intolerance was likely tied to being “fructans”, and that I had discovered I was sensitive to fructans in other foods, was an enzyme powder called Fodzyme. (I have no affiliation with this company, FYI). The powder works to target the FODMAPs in food to help neutralize them so they don’t cause symptoms. It worked for me on the foods I had experimented with, and it allowed me to eat food that had onion powder or garlic powder listed as a minor ingredient (I started small and cautious and am working my way up in testing other foods and different quantities). I longingly wished that there were other enzymes I could take to help improve digestion, because Fodzyme seemed to not only reduce the symptoms I had after I ate, but also seemed to improve my digestion overall (e.g. improved stool formation). I did some research but “digestive enzymes” are generally looked down upon and there’s no good medical research, so I chalked it up to snake oil and didn’t do anything about it.
Until, oddly enough, in November 2021 I noticed a friend’s social media post talking about their dog being diagnosed with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI). It made me go look up EPI in humans to see if it was a thing, because their experience sounded a lot like mine. Turns out, EPI is a thing, and it’s very common in humans who have cystic fibrosis; pancreas-related surgeries or pancreatic cancer; and there is also a known correlation with people with type 1 diabetes or with celiac disease.
Oh hey, that’s me (celiac and type 1 diabetes).
I did more research and found that various studies estimate 40% of people with type 1 diabetes have low levels of pancreatic elastase, which is a proxy for determining if you have insufficient enzymes being produced by your pancreas to help you digest your food. The causal mechanism is unclear, so they don’t know whether it’s just a ‘complication’ and side effect of diabetes and the pancreas no longer producing insulin, or if there is something else going on.
Given the ties to diabetes and celiac, I reached out to my GI doctor again in December 2021 and asked if I should get my pancreatic elastase levels tested to check for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI), given that my symptoms matching the textbook definition and my risk factors of diabetes and celiac. He said sure, sent in the lab request, and I got the lab work done. My results are on the borderline of ‘moderate’ insufficiency, and given my very obvious and long-standing symptoms, and given my GI doc said there would be no harm from trying, I start taking pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (called PERT). Basically, this means I swallow a pill that contains enzymes with the first bite of food that I eat, and the enzymes help me better digest the food I am eating.
And guess what? For me, it works and definitely has helped reduce symptoms after I’m eating and with next-day bathroom habits. So I consider myself to have mild or moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI).
(Also, while I was waiting on my test results to come back, I found that there is a lipase-only version of digestive enzymes available to purchase online, so I got some lipase and began taking it. It involves some titration to figure out how much I needed, but I saw some improvement already from low doses of lipase, so that also led me to want to try PERT, which contains all 3 types of enzymes your pancreas normally naturally produces, even though my elastase levels were on the borderline of ‘moderate’ insufficiency. Not everyone with lower levels of elastase has insufficiency in enzymes, but my symptoms and response to lipase and PERT point to the fact that I personally do have some insufficiency.)
More about my experiences with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Unfortunately, there is no cure for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Like Type 1 diabetes, it requires lifelong treatment. So, I will be taking insulin and now PERT likely for the rest of my life. Lazy pancreas! (Also, it’s possible I will need to increase my PERT dose over time if my insufficiency increases.)
Why treat EPI? Well, beyond managing very annoying symptoms that impact quality of life, if left untreated it’s associated with increased mortality (e.g. dying earlier than you would otherwise) due to malnutrition (because you’re not properly absorbing the nutrients in the food you’re eating) and bone density problems.
Oddly enough, there seem to be two versions of the name (and therefore two acronyms) for the same thing: EPI and PEI, meaning exocrine pancreatic insufficiency or pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. I haven’t found a good explanation for why there are two names and if there are any differences. Luckily, my research into the medical literature shows they both pop up in search results pretty consistently, so it’s not like you end up missing a big body of literature if you use one search term or the other.
Interestingly, I learned 90% of people with cystic fibrosis may need PERT, and thankfully my friend with CF didn’t mind me reaching out to ask her if she had ever taken PERT or had any tips to give me from her knowledge of the CF community. That was nice that it turns out I do know some other people with EPI/PEI, even though they don’t usually talk about it because it seems to go hand in hand with CF. Some of the best resources of basic information about EPI/PEI are written either by CF foundations or by pancreatic cancer-related organizations, because those are the two biggest associated conditions that also link to EPI/PEI. There are also other conditions like diabetes and celiac with strong correlations, but these communities don’t seem to talk about it or have resources focused on it. (As with low FODMAP resources where everything is written for IBS/IBD, you can extrapolate and ignore everything that’s IBS/IBD specific. Don’t be afraid to read EPI/PEI information from communities that aren’t your primary community!)
Sadly, like so many GI conditions (remember in the intro I referenced 7 years average diagnosis time with celiac), it seems ridiculously hard to get to a diagnosis of EPI. I essentially self-diagnosed myself (and confirmed the diagnosis in partnership with my GI doc who agreed to run the tests). I am still very surprised that it never came up on his list of possible conditions despite having symptoms that are textbook EPI and having diabetes and celiac, which are known correlations. Apparently, this is common: I read one study that says even people with super high-risk factors (e.g. pancreas surgery, pancreatic cancer) aren’t necessarily screened, either! So it’s not just me falling through the cracks, and this is something the gastroenterology world needs to be better about. It’s also common for patients to bring this up to their doctors vs their doctors suggesting it as a potential diagnosis – this study found 24% of people brought up EPI, like I did, to their doctors.
Also, unfortunately, I had a few people (including family members) suggest to me in the last two years that my symptoms are psychosomatic, or stress-related. They’re clearly, as proven by lab work, not psychosomatic or stress-related but are a result of my exocrine pancreatic functions failing. Please, don’t ever suggest someone dealing with GI issues is experiencing symptoms due to stress – this is the kind of comment you should keep to yourself. (The last time someone mentioned this to me was months ago, and it still bothers me to think about it.)
Advocate for yourself
One of the very important things I learned early on when living with type 1 diabetes was the importance of knowing my own body, and advocating for myself. This unfortunately was a hard lesson learned, because I had general practice (GP or primary care / PCP) doctors who would refuse to treat me because I had diabetes because they were concerned about prescribing something that would mess up my blood sugars. They’d completely ignore the point that whatever infection I had would cause MORE disruption to my blood sugars by having me be sick and suffer longer, than I would have disruption to my blood sugar levels from a prescription. Sigh. So for the last almost two decades, I have had to go into every health encounter prepared to advocate for myself and make sure I get the medical expertise for whatever I’m there for, and not the less experienced take on diabetes (assuming I wasn’t there for diabetes, which I usually wasn’t).
This has translated into how I approached finding solutions for my GI symptoms. Per my history described above, I had increasing but minor GI symptoms from February-July 2020. Having new, stabbing pains in my abdomen led me to the gastroenterologist for a long list of testing for various things, but I had to continue to push for the next round of testing and schedule and manage everything to proceed through the list we had discussed at my appointment. Later, after we ran through the list, I had to try things like low FODMAP for myself, and then do additional research and identify the test for EPI as a likely next step to try.
I felt a little like the ‘boiling frog’ analogy, where my symptoms gradually worsened over time, but they weren’t startling bad (except for the points in time when I had stabbing abdominal pain). Or the two times, almost one year apart (Oct 2020 and Dec 2021) where I had what I considered bad “flares” of something where I got really hot and feeling really ill all of a sudden, but it wasn’t COVID-19 and it wasn’t anything specific causing it, there were no obvious food triggers, and the only thing I could do was lay down for 2-3 hours and rest before I started to feel better. Those were probably correlated with “overdoing it” with physical activity, but I’ve also run a marathon and a 50k ultramarathon in the last year and didn’t have problems on those days, so there’s not a certain threshold of activity that appears to cause that. Thankfully, that has only happened two times.
Other than those scenarios, it wasn’t like breaking my ankle where there was a clear “everything was fine and now something is broken”, but it was more like “I have had not-good-digestion and various increasing GI symptoms that don’t fit any clear problem or diagnosis on our shortlist of the 5 likely things it might be. It’s not excruciating but it is increasingly impacting my quality of life, and twisting myself into a pretzel with an evolving pattern of dietary modifications is not solving it”. It took me continuing to advocate for myself and not accepting suffering for the rest of my life (hopefully!) with these symptoms to get to an answer, which for me, so far, seems to be moderate exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
What it’s like to start taking pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)
PERT is typically measured by the units/amount of lipase it contains, even though it contains all 3 types of enzymes. (Some of the Medicare documents in different states actually are really helpful for comparing the size of dosing across the different brands of PERT. That also helped me look up the various brands in my insurance plan to see whether there would be a price difference between two of the most common brands.) Depending on symptoms and your level of insufficiency, like insulin, it requires some titration to figure out the right doses. I’ve been attempting to track generally the amount of fat that I’m eating to try to get a sense of my “ratio” of fat to lipase needed, although the research shows there is likely not a linear correlation between grams of fat and units of lipase needed. Another way to think about it is at what level of grams of fat in your meal do you need more than your current dose. For example, one pill of PERT at my current dose seems to work up to around 70 or so grams of fat per meal, as long as it doesn’t have more than 50% protein. Meals containing much more fat (120 g or so) definitely require more, as do meals with either a higher quantity of protein or a closer ratio of 1:1 fat to protein.
Different people have different needs with regard to whether they need enzyme support “just” for fat, or also for protein and carbs. I appear to at least need some support for carbs as well as protein, but am still establishing at what levels I need which dosing of which enzymes.
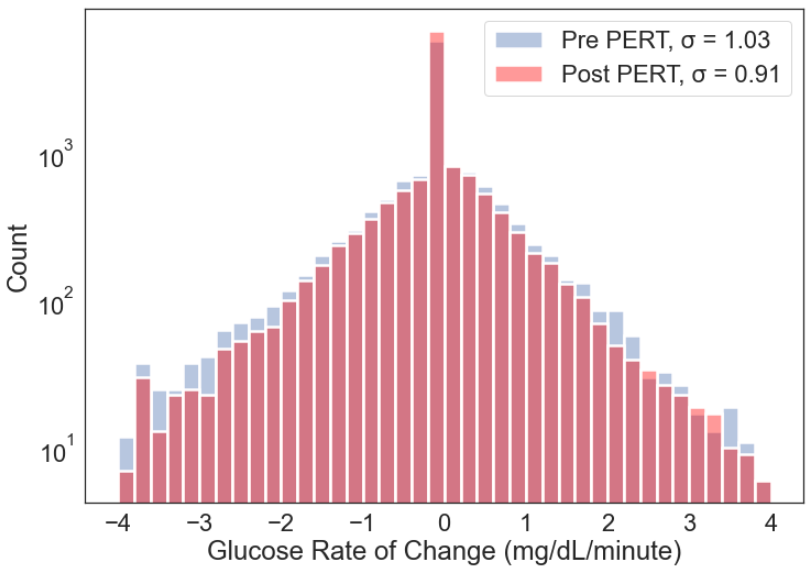
Personally, I am tracking to see whether my symptoms are reduced or eliminated in the hours following my meals (gas, abdominal discomfort, a sick feeling after eating) as well as the next day (bloating/abdominal distension, bathroom habits such as reduced steatorrhea), and overall whether I have any more of those really bad “flares”. My initial tests of taking PERT show improvements after my meals (I don’t feel sick after I eat anymore!) and often the next day.
After the first few days of trying food that was low FODMAP but giving me minor symptoms before PERT, I’ve also felt confident enough to try meals that I’ve avoided eating for over a year, such as a gluten free burger from one of our nearby local favorites! Even though it’s been well over a year since I’ve had it last, I immediately could tell a difference in how I felt eating it, due to taking PERT with it. There was no wave of fatigue before I was halfway through the burger, and no gas or feeling sick to my stomach after eating. I had clearly forgotten what it was like to not feel miserable after eating and to actually enjoy eating food! So far, PERT has been exceeding my expectations (although those were rather low).
It makes it slightly less annoying, then, to think about the price of PERT. Roughly, one month of PERT at the dosage I’m currently on costs the same as 3 vials of insulin in the US (in the ballpark of $800). Like insulin, PERT is necessary and worthwhile (and thankfully I do have health insurance).
Pancreases are great when they work…and expensive to replace!

—
TLDR: I have a new thing, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, to deal with. Thankfully, there’s a treatment (PERT) that I can use to reduce symptoms and hopefully limit the potential impacts on morbidity long term. If you have diabetes or celiac and you have unexplained GI symptoms over time, you might want to do some research into EPI and discuss it with your gastroenterologist.
Also…for any endocrinologist reading this…or any other healthcare providers…if you have patients with diabetes and suspected GI issues, please consider EPI as a possible diagnosis once you’ve ruled out celiac disease and other likely suspects. Given the high rates of lowered elastase in all types of diabetes, it’s worth screening for EPI in patients with otherwise-unexplained steatorrhea or similar symptoms.
—
PS – if you land on this post and haven’t seen it already, you may want to check out PERT Pilot, the first iOS app for Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency! It’s an iOS app that I built that allows you to record as many meals as you want, the PERT dosing and outcomes, to help you visualize and review more of your PERT dosing data!
—
You can also contribute to a research study and help us learn more about EPI/PEI – take this anonymous survey to share your experiences with EPI-related symptoms!
—


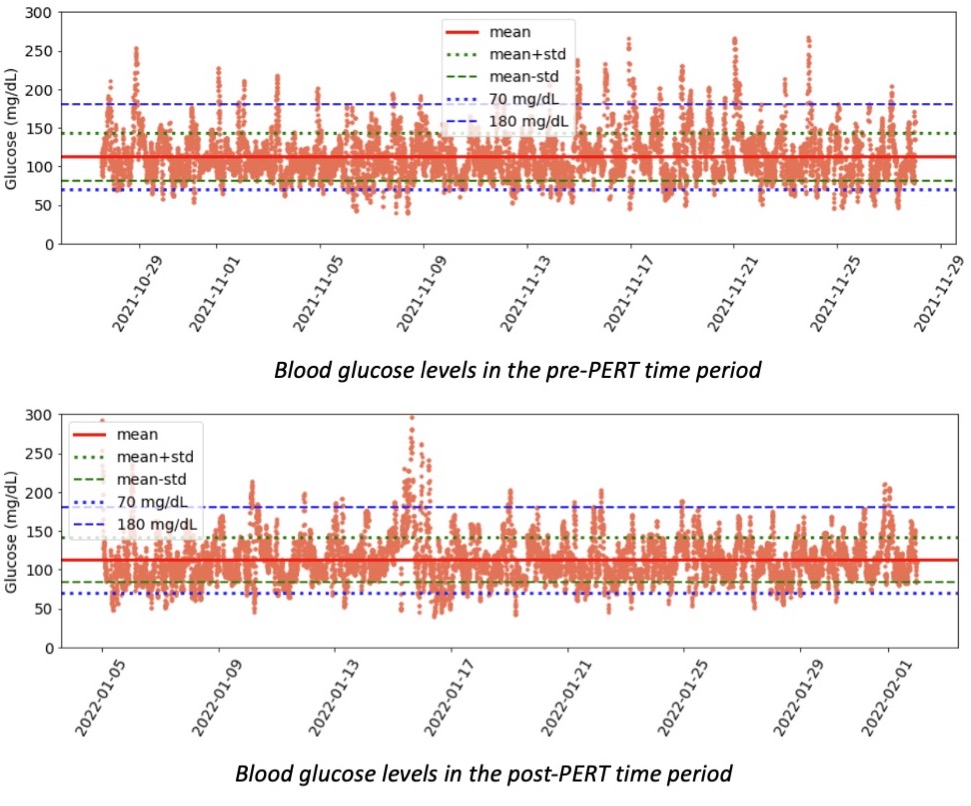
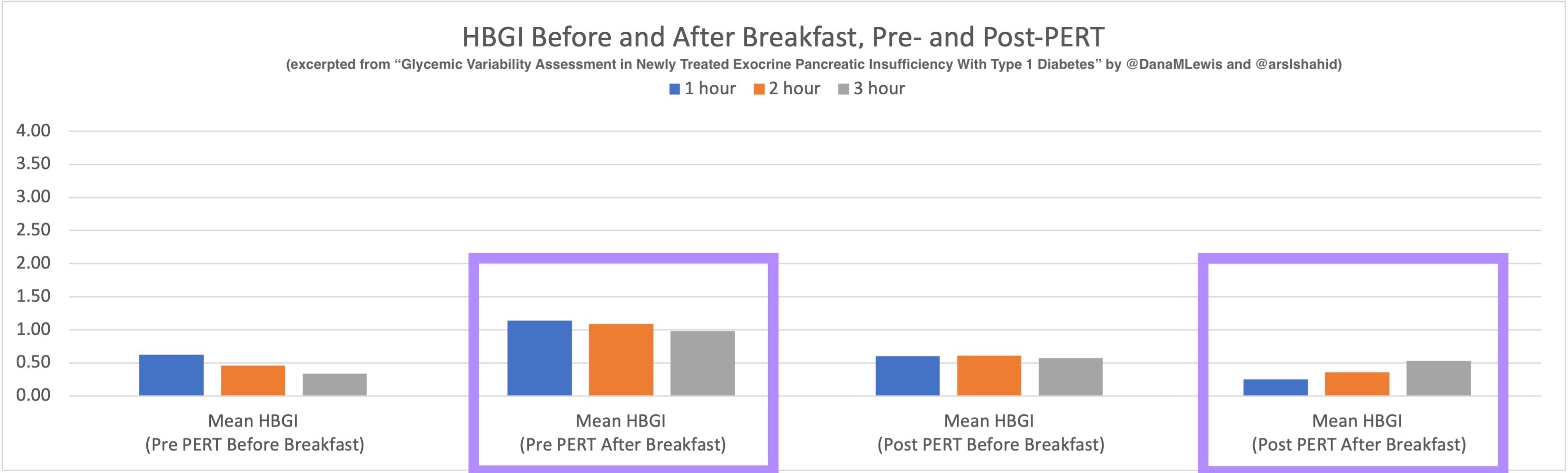
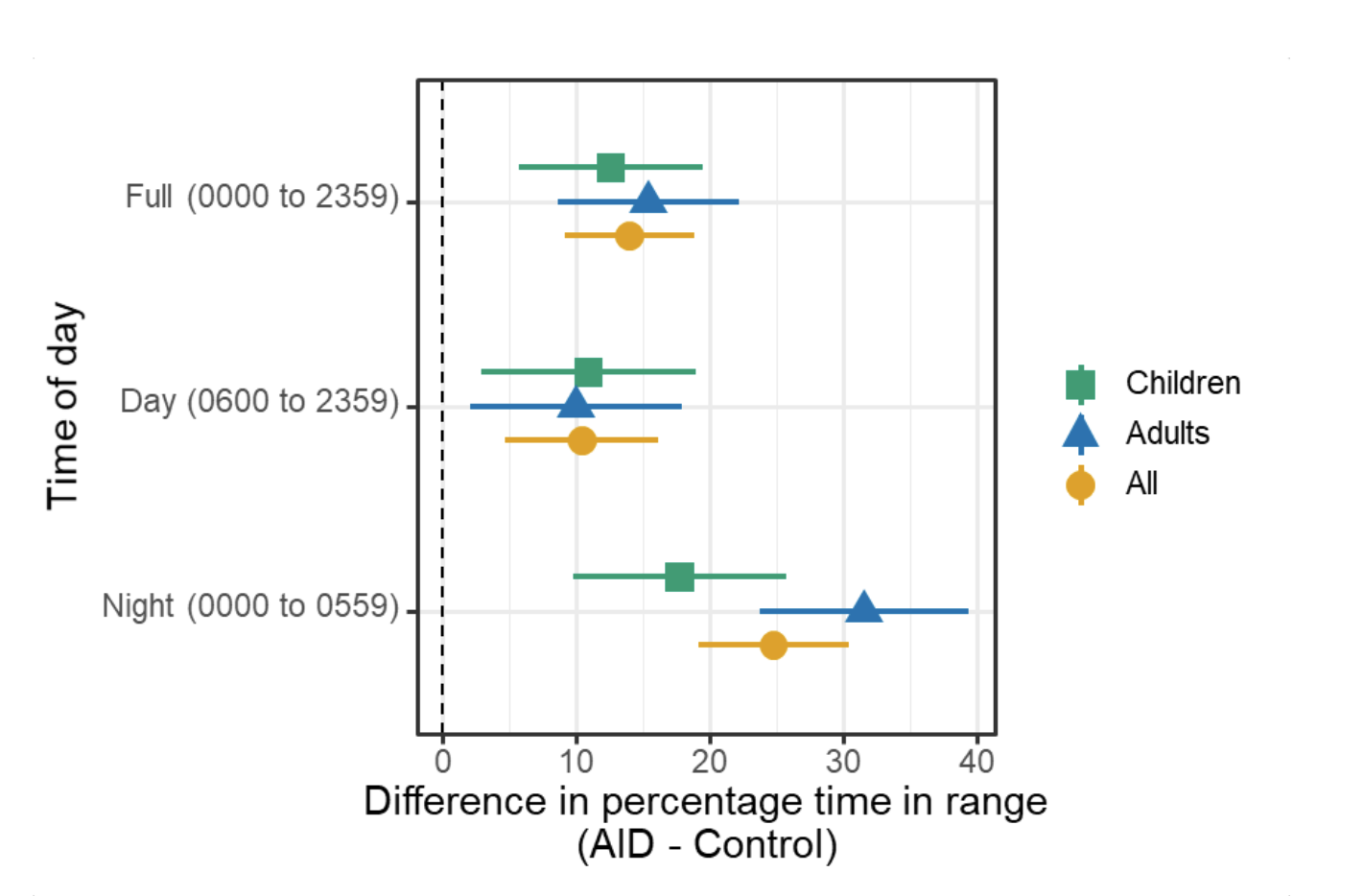





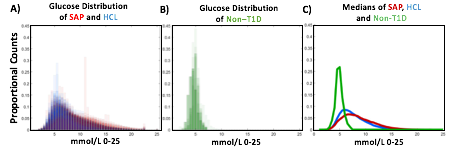
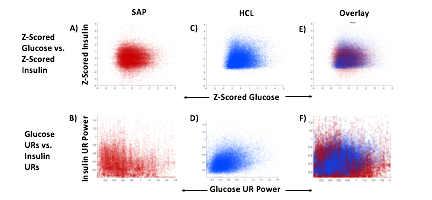
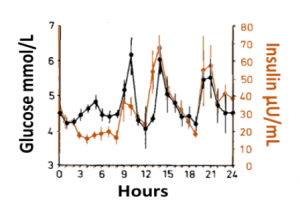 Blood glucose and insulin exhibit coupled biological rhythms at multiple timescales, including hours (ultradian, UR) and the day (circadian, CR) in individuals without diabetes. The presence and stability of these rhythms are associated with healthy glucose control in individuals without diabetes. (See right, adapted from
Blood glucose and insulin exhibit coupled biological rhythms at multiple timescales, including hours (ultradian, UR) and the day (circadian, CR) in individuals without diabetes. The presence and stability of these rhythms are associated with healthy glucose control in individuals without diabetes. (See right, adapted from 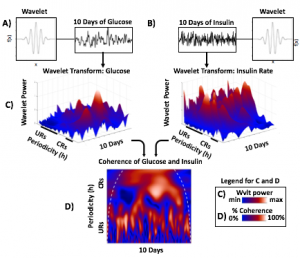
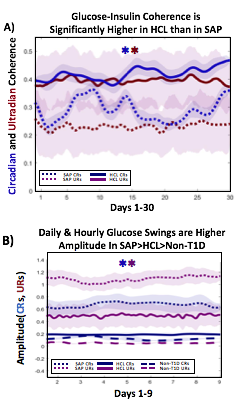 A) Circadian (blue) and 3-6 hour ultradian (maroon) coherence of glucose and insulin in HCL (solid) and SAP (dotted) users. Transparent shading indicates standard deviation. Although both HCL and SAP individuals have lower coherence than would be expected in a non-T1D individual, HCL CR and UR coherence are significantly greater than SAP CR and UR coherence (paired t-test p= 1.51*10-7 t=-5.77 and p= 5.01*10-14 t=-9.19, respectively). This brings HCL users’ glucose and insulin closer to the canonical non-T1D phenotype than SAP users’.
A) Circadian (blue) and 3-6 hour ultradian (maroon) coherence of glucose and insulin in HCL (solid) and SAP (dotted) users. Transparent shading indicates standard deviation. Although both HCL and SAP individuals have lower coherence than would be expected in a non-T1D individual, HCL CR and UR coherence are significantly greater than SAP CR and UR coherence (paired t-test p= 1.51*10-7 t=-5.77 and p= 5.01*10-14 t=-9.19, respectively). This brings HCL users’ glucose and insulin closer to the canonical non-T1D phenotype than SAP users’.

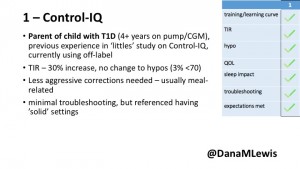
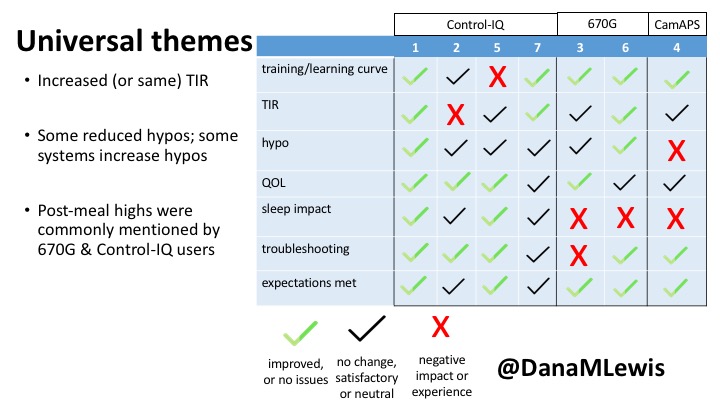
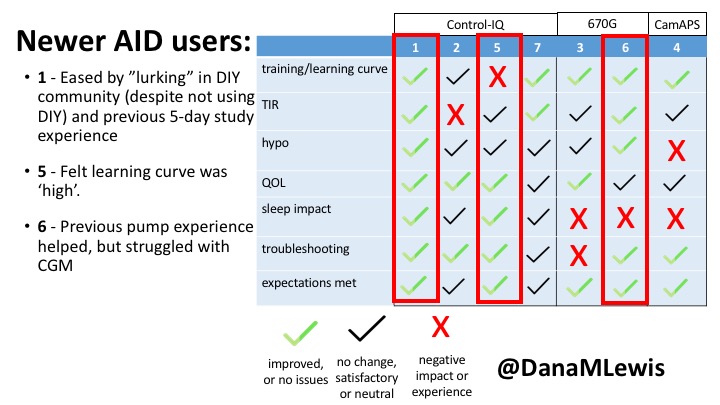
 1 – A parent of a child using Control-IQ (off-label), with 30% increase in TIR with no increased hypoglycemia. They spend less time correcting than before; less time thinking about diabetes; and “get solid uninterrupted sleep for the first time since diagnosis”. They wish they had remote bolusing, more system information available in remote monitoring on phones. They miss using the system during the 2 hour CGM warmup, and found the system dealt well with growth spurt hormones but not as well with underestimated meals.
1 – A parent of a child using Control-IQ (off-label), with 30% increase in TIR with no increased hypoglycemia. They spend less time correcting than before; less time thinking about diabetes; and “get solid uninterrupted sleep for the first time since diagnosis”. They wish they had remote bolusing, more system information available in remote monitoring on phones. They miss using the system during the 2 hour CGM warmup, and found the system dealt well with growth spurt hormones but not as well with underestimated meals.
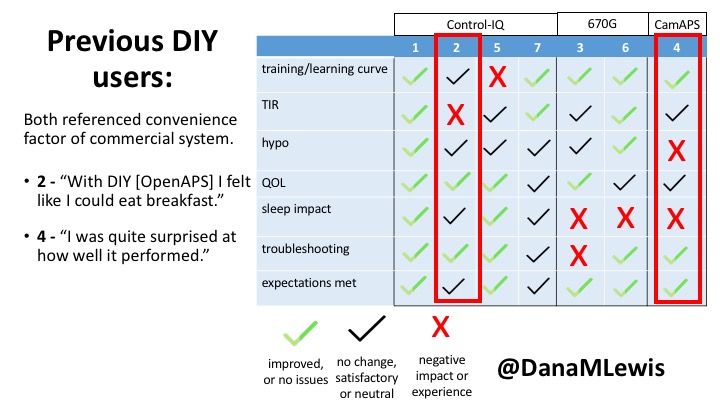
 2 – An adult male with T1D who previously used DIYAPS saw 5-10% decrease in TIR (but it’s on par with other participants’ TIR) with Control-IQ, and is very pleased by the all-in-one convenience of his commercial system.He misses autosensitivity (a short-term learning feature of how insulin needs may very from base settings) from DIYAPS and has stopped eating breakfast, since he found it couldn’t manage that well. He is doing more manual corrections than he was before.
2 – An adult male with T1D who previously used DIYAPS saw 5-10% decrease in TIR (but it’s on par with other participants’ TIR) with Control-IQ, and is very pleased by the all-in-one convenience of his commercial system.He misses autosensitivity (a short-term learning feature of how insulin needs may very from base settings) from DIYAPS and has stopped eating breakfast, since he found it couldn’t manage that well. He is doing more manual corrections than he was before.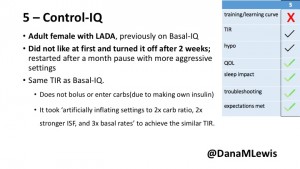
 5 – An adult female with LADA started, stopped, and started using Control-IQ, getting the same TIR that she had before on Basal-IQ. It took artificially inflating settings to achieve these similar results. She likes peace of mind to sleep while the system prevents hypoglycemia. She is frustrated by ‘too high’ target; not having low prevention if she disables Control-IQ; and how much she had to inflate settings to achieve her outcomes. It’s hard to know how much insulin the system gives each hour (she still produces some of own insulin).
5 – An adult female with LADA started, stopped, and started using Control-IQ, getting the same TIR that she had before on Basal-IQ. It took artificially inflating settings to achieve these similar results. She likes peace of mind to sleep while the system prevents hypoglycemia. She is frustrated by ‘too high’ target; not having low prevention if she disables Control-IQ; and how much she had to inflate settings to achieve her outcomes. It’s hard to know how much insulin the system gives each hour (she still produces some of own insulin).
 7 – An adult female with T1D who frequently has to take steroids for other reasons, causing increased BGs. With Control-IQ, she sees 70% increase in TIR overall and increased TIR overnight, and found it does a ‘decent job keeping up’ with steroid-induced highs. She also wants to run ‘tighter’ and have an adjustable target, and does not ever run in sleep mode so that she can always get the bolus corrections that are more likely to bring her closer to target.
7 – An adult female with T1D who frequently has to take steroids for other reasons, causing increased BGs. With Control-IQ, she sees 70% increase in TIR overall and increased TIR overnight, and found it does a ‘decent job keeping up’ with steroid-induced highs. She also wants to run ‘tighter’ and have an adjustable target, and does not ever run in sleep mode so that she can always get the bolus corrections that are more likely to bring her closer to target.
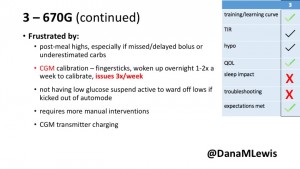 3 – An adult male with T1D using 670G for 3 years didn’t observe any changes to A1c or TIR, but is pleased with his outcomes, especially with the ability to handle his activity levels by using the higher activity target. He is frustrated by the CGM and is woken up 1-2x a week to calibrate overnight. He wishes he could still have low glucose suspend even if he’s kicked out of automode due to calibration issues. He also commented on post-meal highs and more manual interventions.
3 – An adult male with T1D using 670G for 3 years didn’t observe any changes to A1c or TIR, but is pleased with his outcomes, especially with the ability to handle his activity levels by using the higher activity target. He is frustrated by the CGM and is woken up 1-2x a week to calibrate overnight. He wishes he could still have low glucose suspend even if he’s kicked out of automode due to calibration issues. He also commented on post-meal highs and more manual interventions.
 6 – Another adult male user with 670G was originally diagnosed with T2 (now considered T1) with a very high total daily insulin use that was able to decrease significantly when switching to AID. He’s happy with increased TIR and less hypo, plus decreased TDD. Due to #COVID19, he did virtually training but would have preferred in-person. He has 4-5 alerts/day and is woken up every other night due to BG alarms or calibration. He does not like the time it takes to charge CGM transmitter, in addition to sensor warmup.
6 – Another adult male user with 670G was originally diagnosed with T2 (now considered T1) with a very high total daily insulin use that was able to decrease significantly when switching to AID. He’s happy with increased TIR and less hypo, plus decreased TDD. Due to #COVID19, he did virtually training but would have preferred in-person. He has 4-5 alerts/day and is woken up every other night due to BG alarms or calibration. He does not like the time it takes to charge CGM transmitter, in addition to sensor warmup.
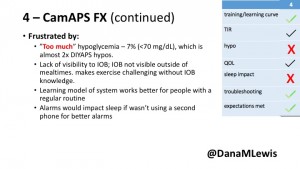 4 – The last participant is an adult male with T1 who previously used DIYAPS but was able to test-drive the CamAPS FX. He saw no TIR change to DIYAPS (which pleased him) and thought the learning curve was easy – but he had to learn the system and let it learn him. He experienced ‘too much’ hypoglycemia (~7% <70mg/dL, 2x his previous), and found it challenging to not have visibility of IOB. He also found the in-app CGM alarms annoying. He noted the system may work better for people with regular routines.
4 – The last participant is an adult male with T1 who previously used DIYAPS but was able to test-drive the CamAPS FX. He saw no TIR change to DIYAPS (which pleased him) and thought the learning curve was easy – but he had to learn the system and let it learn him. He experienced ‘too much’ hypoglycemia (~7% <70mg/dL, 2x his previous), and found it challenging to not have visibility of IOB. He also found the in-app CGM alarms annoying. He noted the system may work better for people with regular routines.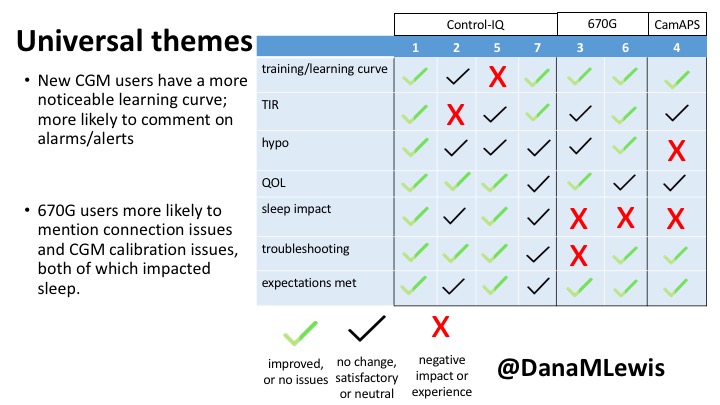


Recent Comments