I’ve been taking thyroid medication for a few months now. It surprised me how quickly I saw some symptom resolution. As I wrote previously, I started taking thyroid medication and planned to get more lab work at the 8 week mark.
The theory is that thyroid medication influences the production of new thyroid hormones but not the stored thyroid hormones; thus, since it takes around 6 weeks for you to replace your stores of thyroid hormones, you usually get blood work no sooner than 6 weeks after making a change to thyroid medication.
I had noted, though, that some of my symptoms included changes in my heart rate (HR). This was both my overnight resting HR and how my HR felt during the day. I had hypothesized:
Given I have a clear impact to my heart rate, I’m hypothesizing that I might see changes to the trend in my heart rate data sooner than 6 weeks – 2 months, so that’ll be interesting to track!
This turned out to be an accurate prediction!
My provider had suggested starting me on a low dose of “antithyroid” medication. Guidelines typically suggest 10-20mg per day, with plans to titrate (adjust) the dose based on how things are going. However, in my case, I have subclinical hyperthyroidism – not actual hyperthyroidism – which means my thyroid levels themselves (T3 and T4) were in range. What was out of range for me was my thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which was below range, and my thyroid antibodies, all of which were above range. (If you want to read about my decision making and my situation with Graves’ disease with eye symptoms and subclinical hyperthyroidism, read my previous post for more details.)
I ended up being prescribed a 5mg dose. Thinking about it, given my T3 and T4 were well within range, that made sense. I started taking it in early August.
What it felt like to start taking antithyroid medication for the first time:
For context, my primary most bothersome symptoms were eye symptoms (eyelid swelling, sometimes getting a red patchy dry area outside the outer corner of my eye, eye pressure that made me not want to wear my contacts); increased resting overnight HR and higher HR during periods of rest during the day; and possibly mood and energy impacts.
- Within a week (!) of starting the antithyroid medication, my overnight HR began lowering. This can be influenced by other factors like exercise etc., but it was also accompanied by fewer days with higher heart rate while I was sitting and relaxing! I definitely felt a noticeable improvement within a week of my heart rate-related symptoms.
- My eyelid swelling went away toward the end of the first week. Then after 3 or so days, it came back again for a few days, then went away for 12 days. It came back for several days, went away for another 6 days. Came back, then…nothing! I went weeks without eyelid swelling and none of the other eye-related symptoms that typically ebbed and flowed alongside the eyelid swelling. HOORAY!
- It’s unclear how much my mood and energy were directly effected by the wonky thyroid antibody levels compared to being a correlation with the symptoms themselves. (I was also resuming ultramarathon training during this time period, following the recovery of my broken toe.) However, I definitely was feeling more energetic and less grumpy, as noticed by my husband as well.
What is interesting to me is that my symptoms were changed within a week. They often talk in the medical literature about not knowing exactly how the thyroid medication works. In my case, it’s worth noting again for context that I had subclinical hyperthyroidism (in range T3 and T4 but below range TSH) and Graves’ disease (several thyroid antibodies well above range) with correlated eye symptoms. The theory is that the eye symptoms are influenced by the thyroid antibody levels, not the thyroid levels (T3 and T4) themselves. So although the thyroid medication influences the production of new thyroid hormones and it takes 6 weeks to replace your store of thyroid hormones; my working hypothesis is that the symptoms driven by TSH and thyroid antibodies are influenced by the production of those (rather than the stores) and that is why I see a change to my symptoms within a week or so of starting thyroid medication.
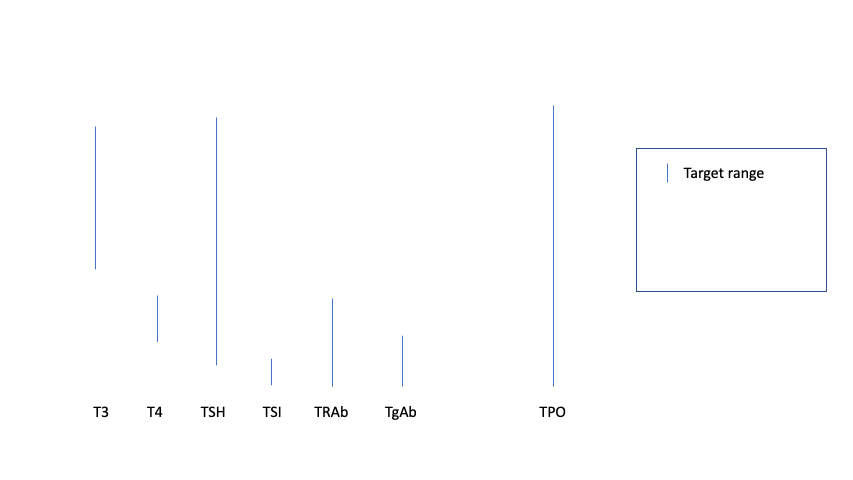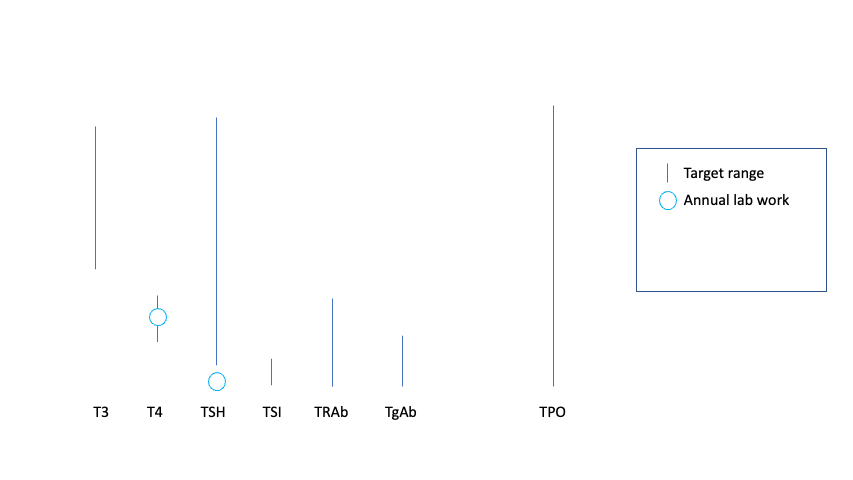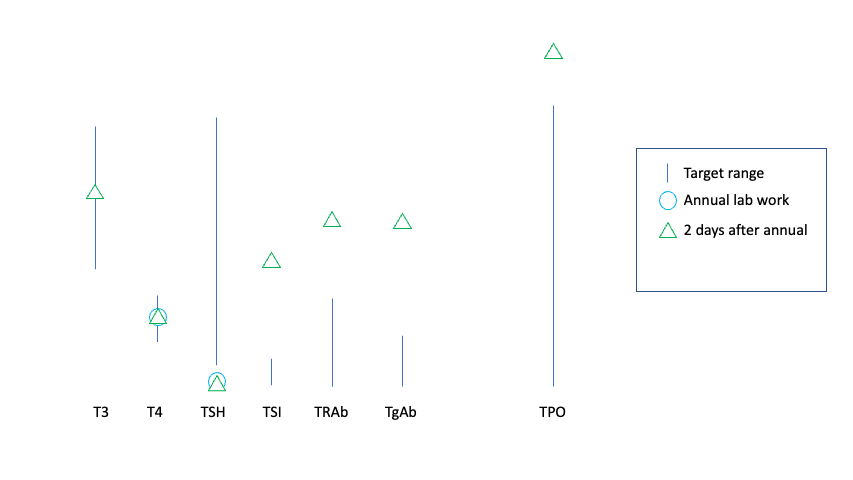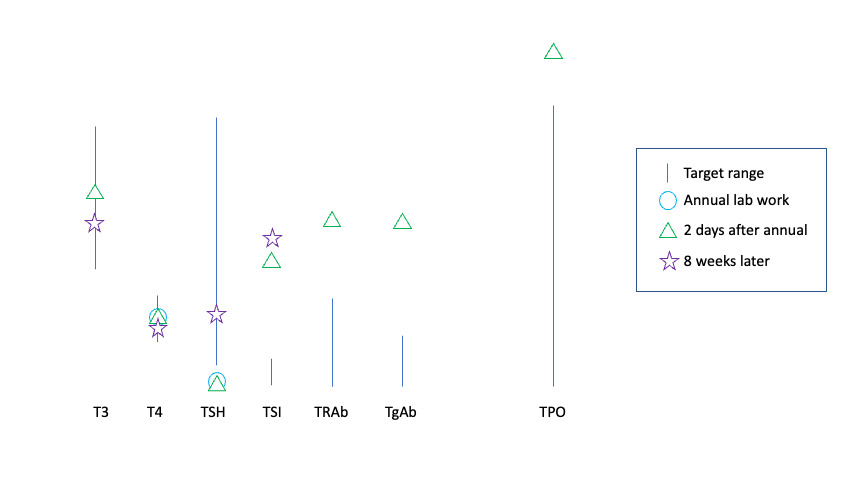
I went for repeat lab work at 8 weeks, and I was pretty confident that I would have improved antibody and TSH levels. I wasn’t sure if my T3 and T4 would drop below range or not. The lab work came back in and… I was right! TSH was back to normal range (HOORAY), T3 and T4 were slightly lower than the previous numbers but still nicely in the middle of the range. Yay! However, my TSI (thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin) was still well above range, and slightly higher than last time. Boo, that was disappointing, because there are some studies (example) showing that out of range TSI can be a predictor for those with Graves’ disease for the need to continue antithyroid medication in the future.
As I wrote in my last post:
I am managing my expectations that managing my thyroid antibody and hormone levels will be an ongoing thing that I get to do along with managing insulin and blood sugars and managing pancreatic enzymes. We’ll see!
The TSI was a pointer that although I had reduced all of my symptoms (hooray) and my T3 and T4 were within range, I would probably need ongoing medication to keep things in range.
However, as a result of the lab work, my provider suggested dropping down to 2.5mg dose, to see if that would manage my thyroid successfully without pushing me over to hypothyroidism (low T3 and T4) levels, which can be a risk of taking too much antithyroid medication. He suggested switching to 2.5mg, and repeating lab work in 3 months or if I felt unwell.
I agreed that it was worth trying, but I was a little nervous about reducing my dose, because my T3 and T4 were still well within the middle of normal. And, I had an upcoming very long ultramarathon. Given that with the start of thyroid medication I saw symptoms change within a week, and I was two weeks out from my ultra, I decided to wait until after the ultramarathon so I could more easily monitor and assess any symptoms separately from the taper and ultra experience.
Recovery from my ultramarathon was going surprisingly well, enough so that I felt ready to switch the medication levels pretty soon after my ultra. I started taking the 2.5mg dose (by cutting the 5mg dose in half, as I had some remaining and it was easier than ordering a changed prescription to 2.5mg).
I carefully watched and saw some slight changes to my HR within the first week. But, I was also recovering from an ultramarathon, and that can also influence HR. Again, I was looking at both the overnight resting HR and noting any periods of time during the day where I was resting when my HR was high (for me). I had two days where it did feel high during the day, but the following days I didn’t observe it again, so I chalked that up to maybe being related to ultramarathon recovery.
But a little over a week and my right eye started feeling gunky. I had just been to the eye doctor for my annual exam and all was well and my eye didn’t look red or irritated. I didn’t think much of it. But a few days after that, I had rubbed my right eyelid and realized it felt poofy. I felt my left eyelid in comparison, and the right was definitely swollen in comparison. Looking in the mirror, I could see the swollen eyelid pushing down the corner of my right eye. Just like it had done before I started thyroid medications. Ugh. So eye symptoms were back. A few days later, I also woke up feeling like my eyes hurt and they needed lubrication (eye drops) as soon as I opened my eyes. That, too, had been a hallmark of my eye symptoms from last October onward.
The plan had been to wait until 3 months after this medication change to repeat labs. I’m going to try to wait until the 6-8 week mark again, so we can see what the 2.5mg does to my T3 and T4 levels alongside my TSH. But, my prediction for this next round of lab work is that T3 and T4 will go up (maybe back to the higher end but likely still within range; although the possibility to fully go above range), and that my TSH will have dropped back down below range, because the symptom pattern I am starting to have mimics the symptom pattern I had for months prior to starting the 5mg thyroid medication.
Why only wait 6-8 weeks, when my provider suggested 3 months?
These symptoms are bothersome. The eyelid swelling thankfully subsided somewhat after 4 days (after the point where it got noticeable enough for my husband to also see it compressing my outer corner of my eye, which means anyone would be able to visibly see it), but I’m watching it to see if it returns with a cyclical pattern the way it went away previously, expecting it to likely return to constant every day eye swelling. Since it influences my vision slightly (because the eyelid is pushed down by the swelling), that impacts my quality of life enough to take action sooner. If it gets really bad, I might discuss with my provider and get labs even sooner, but I’m going to try to tough it out to 6-8 weeks to get a full picture of data of how the 2.5mg impacted all of my levels and also see what pattern of symptoms return when, because it will be interesting to compare the symptom levels at 5mg (essentially all gone within 1-2 weeks) and at 2.5mg compared to my original, pre-thyroid medication symptom levels and patterns.
But depending on those labs, I predict that I will return to taking the 5mg dose, and hopefully my symptoms will go away completely and stay away. Then it’ll be a future decision on if/when to try titrating down again; possibly guided by the TSI level, since the TSI was still above range when we had switched me to 2.5mg (despite the change in TSH back to range).
The good news is, though, that in future I should be able to use the 1-2 weeks of symptom data to determine whether a change in dose is working for me or not, instead of having to wait a full 6-8 weeks, because my symptoms seem to be driven by the TSH and antibody levels, rather than out of range T3 and T4 levels (because they were and are still in the middle of the goal range).
I also discussed this with my eye doctor. You’ll note from my previous post that I was very concerned about the eye impacts and symptoms, so I had asked my eye doctor if she’s still comfortable treating me (she is), and we talked about what things would cause me to get a referral to a specialist. So far my symptoms don’t seem on track for that; it would be my eyes protruding from the socket and having pressure that would possibly need surgery. Disappointingly, she confirmed that there’s really no treatment for the symptoms since they’re caused by the antibody levels. There’s no anti-swelling stuff to put on my eyelid to help. Instead, the goal is to manage the antibody levels so they don’t cause the symptoms. (Which is everything I’m talking about doing above, including likely returning to the 5mg dose given that my eye symptoms resumed on the 2.5mg dose).
—
In summary, I think it is worth noting for anyone with Graves’ disease (whether or not they have subclinical or actual hyperthyroidism) that it is possible to see symptom changes within a week or two of starting or changing your thyroid medication. I can’t find anything in the literature tracking symptom resolution on anything shorter than a 6 week time period, but maybe in the future someone will design a study to capture some of the real-world data and/or run a prospective study to capture this data and see how prevalent this is for symptoms to resolve on a much shorter time frame, for those of us whose symptoms are driven not by thyroid levels themselves (T3 and T4) but for the TSH and TSI and other thyroid antibodies (TPO etc).
If you do start thyroid medication, it’s worth logging your symptoms as soon as possible, ideally before you start your medication, or if it’s too late for that, start logging them afterward. You can then use that as a comparison in the future for if you reduce, increase, or are directed to stop taking your medication, so you can see changes in the length of time it takes to develop or reduce symptoms and whether the patterns of symptoms change over time.


Recent Comments