I recently ran my second-ever 50k ultramarathon. This is my attempt to provide a race recap or “race report”, which in part is to help people in the future considering this race and this course. (I couldn’t find a lot of race reports investigating this race!)
It’s also an effort to provide an example of how I executed fueling, enzyme dosing (because I have exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, known as EPI), and blood sugar management (because I have type 1 diabetes), because there’s also not a lot of practical guidance or examples of how people do this. A lot of it is individual, and what works for me won’t necessarily work for anyone, but if anything hopefully it will help other people feel not alone as they work to figure out what works for them!
Context of my running and training in preparation
I wrote quite a bit in this previous post about my training last year for a marathon and my first 50k. Basically, I’m slow, and I also choose to run/walk for my training and racing. This year I’ve been doing 30:60 intervals, meaning I run 30 seconds and walk 60 seconds.
Due to a combination of improved training (and having a year of training last year), as well as now having recognized I was not getting sufficient pancreatic enzymes so that I was not digesting and using the food I was eating effectively, this year has been going really well. I ended up training as far as a practice 50k about 5 weeks out from my race. I did several more mid- to high-20 mile runs as well. I also did a next-day run following my long runs, starting around 3-4 miles and eventually increasing to 8 miles the day after my 50k. The goal of these next-day runs was to practice running on tired legs.
Overall, I think this training was very effective for me. My training runs were easy paced, and I always felt like I could run more after I was done. I recovered well, and the next-day runs weren’t painful and I did not have to truncate or skip any of those planned runs. (Previous years, running always felt hard and I didn’t know what it was like to recover “well” until this year.) My paces also increased to about a minute/mile faster than last year’s easy pace. Again, that’s probably a combination of increased running overall and better digestion and recovery.
Last year I chose to run a marathon and then do a 50k while I was “trained up” for my marathon. This year, I wanted to do a 50k as a fitness assessment on the path to a 50 mile race this fall. I looked for local-ish 50k options that did not have much elevation, and found the Strawberry Fields Forever Ultra.
Why I chose this race, and the basics about this race
The Strawberry Fields Forever Ultra met most of my goal criteria, including that it was around the time that I wanted to run a 50k, so that I had almost 6 months to train and also before it got to be too hot and risked being during wildfire smoke season. (Sadly, that’s a season that now overlaps significantly with the summers here.) It’s local-ish, meaning we could drive to it, although we did spend the night before the race in the area just to save some stress the morning of the race. The race nicely started at 9am, and we drove home in the evening after the race.
The race is on a 10k (6.2 miles) looped course in North Bonneville, Washington, and hosted a 10k event (1 lap), a 50k event (5 laps), and also had 100k (10 laps) or (almost) 100 miles (16 laps). It does have a little bit of elevation – or “little” by ultramarathon standards. The site and all reports describe one hill and net 200 feet of elevation gain and loss. I didn’t love the idea of a 200 foot hill, but thought I could make do. It also describes the course as “grass and dirt” trails. You’ll see a map later where I’ve described some key points on the course, and it’s also worth noting that this course is very “crew-able”. Most people hang out at the start/finish, since it’s “just” a 10k loop and people are looping through pretty frequently. However, if you want to, either for moral or practical support, crew could walk over to various points, or my husband brought his e-bike and biked around between points on the course very easily using a mix of the other trails and actual roads nearby.
The course is well marked. Any turn had a white sign with a black arrow on it and also white arrows drawn on the ground, and there were dozens of little red/pink fluorescent flags marking the course. Any time there was a fork in the path, these flags (usually 2-3 for emphasis, which was excellent for tired brains) would guide you to the correct direction.
The nice thing about this race is it includes the 100 mile option and that has a course limit of 30 hours, which means all the other distances also have this course limit of 30 hours. That’s fantastic when a lot of 50k or 50 mile (or 100k, which is 62 miles) courses might have 12 hour or similar tighter course limits. If you wanted to have a nice long opportunity to cover the distance, with the ability to stop and rest (or nap/sleep), this is a great option for that.
With the 50k, I was aiming to match or ideally beat my time from my first 50k, recognizing that this course is harder given the terrain and hill. However, I think my fitness is higher, so beating that time even with the elevation gain seemed reasonable.
Special conditions and challenges of the 2022 Strawberry Fields Forever Ultramarathon
It’s worth noting that in 2021 there was a record abnormal heat wave due to a “heat dome” that made it 100+ degrees (F) during the race. Yikes. I read about that and I am not willing to run a race when I have not trained for that type of heat (or any heat), so I actually waited until the week before the race to officially sign up after I saw the forecast for the race. The forecast originally was 80 F, then bounced around mid 60s to mid 70s, all of which seemed doable. I wouldn’t mind some rain during the race, either, as rainy 50s and 60s is what I’ve been training in for months.
But just to make things interesting, for the 2022 event the Pacific Northwest got an “atmospheric river” that dumped inches of rain on Thursday..and Friday. Gulp. Scott and I drove down to spend the night Friday night before the race, and it was dumping hard rain. I began to worry about the mud that would be on the course before we even started the race. However, the rain finished overnight and we woke up to everything being wet, but not actively raining. It was actually fairly warm (60s), so even if it drizzled during the race it wouldn’t be chilly.
During the start of the race, the race director said we would get wet and joked (I thought) about practicing our backstroke. Then the race started, and we took off.
My race recap / race report the 2022 Strawberry Fields Forever Ultramarathon
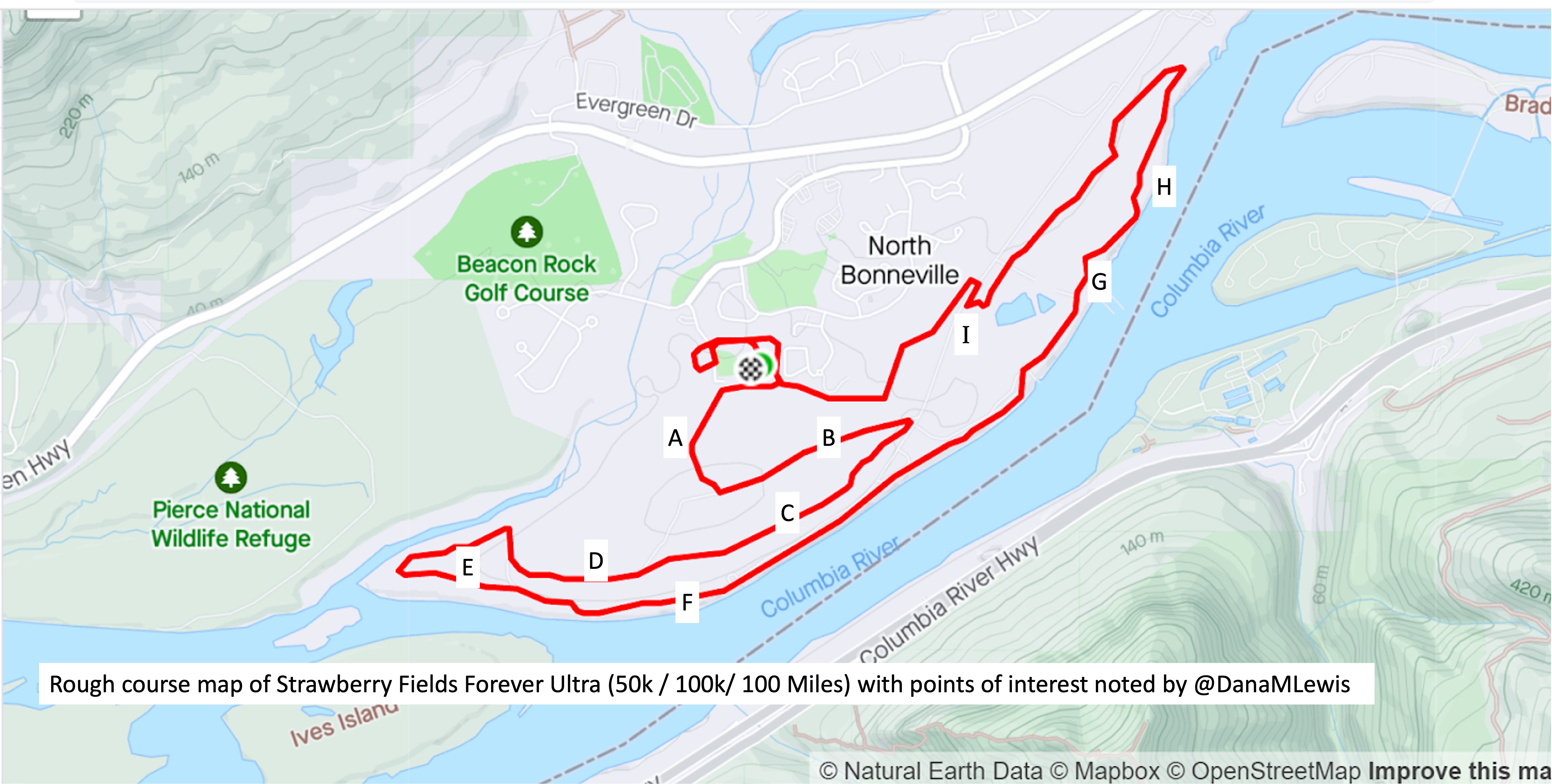
I’ve included a picture below that I was sent a month or so before the race when I asked for a course map, and a second picture because I also asked for the elevation profile. I’ve marked with letters (A-I) points on the course that I’ll describe below for reference, and we ran counterclockwise this year so the elevation map I’ve marked with matching letters where “A” is on the right and “I” is on the left, matching how I experienced the course.
The course is slightly different in the start/finish area, but otherwise is 95% matching what we actually ran, so I didn’t bother grabbing my actual course map from my run since this one was handy and a lot cleaner than my Runkeeper-derived map of the race.
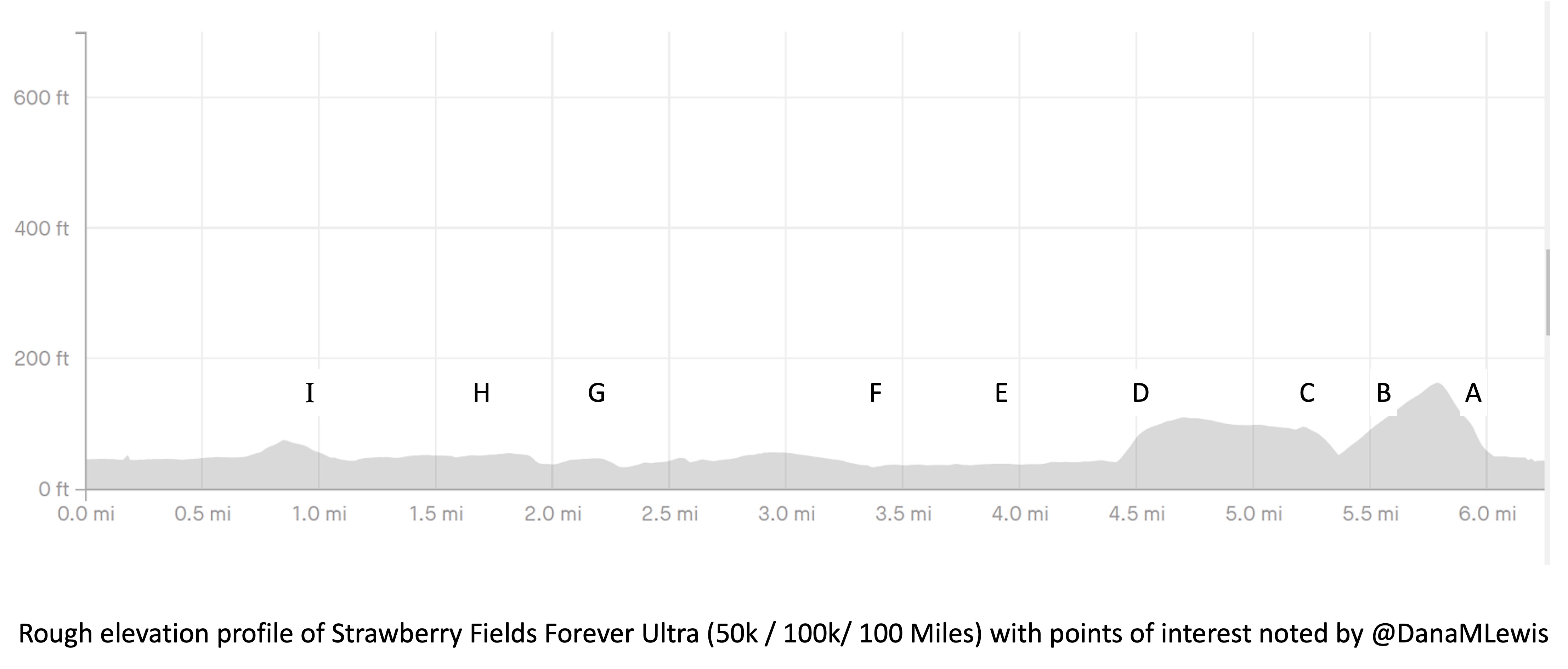
My Runkeeper elevation profile of the 50k (5 repeated laps) looked like this:
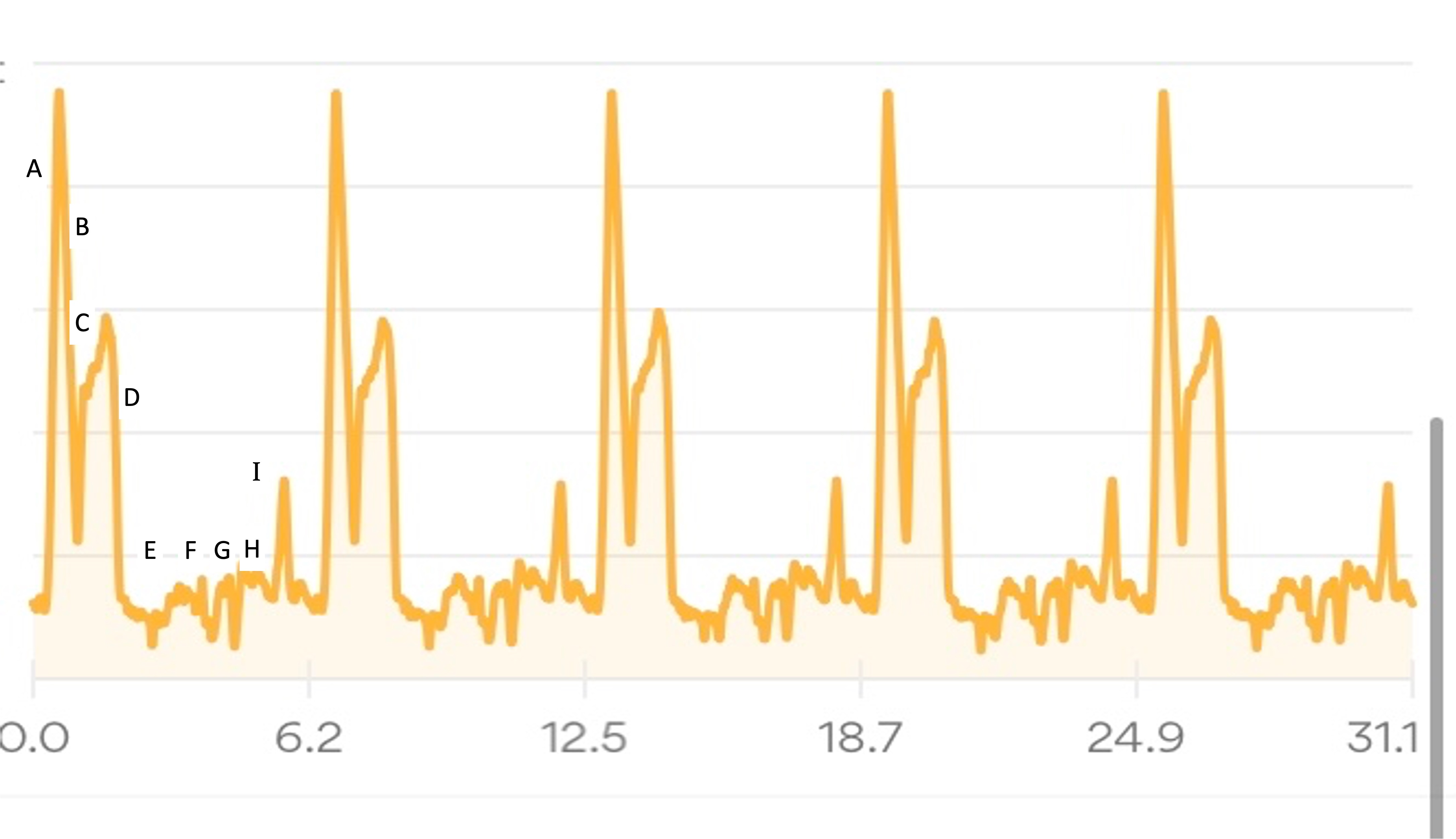
I’ll describe my first experience through the course (Lap 1) in more detail, then a couple of thoughts about the experiences of the subsequent laps, in part to describe fueling and other choices I made.
Lap 1:
We left the start by running across the soccer field and getting on a paved path that hooked around the ballfield and then headed out a gate and up The Hill. This was the one hill I thought was on the course. I ran a little bit and passed a few people who walked on a shallower slope, then I also converted to a walk for the rest of the hill. It was the most crowded race start I’ve done, because there were so many people (150 across the 10k, 50k, 100k, and 100 miler) and such a short distance between the start and this hill. The Hill, as I thought of it, is point A on the course map.
Luckily, heading up the hill there are gorgeous purple wildflowers along the path and mountain views. At the top of the hill there are some benches at the point where we took a left turn and headed down the hill, going down the same elevation in about half a mile so it was longer than the uphill section. This downhill slope (B) was very runnable and gravel covered, whereas going up the hill was more dirt and mud.
At the bottom of the hill, there was a hairpin turn and we turned and headed back up the hill, although not all the way up, and more along a plateau in the side of the hill. The “plateau” is point C on the map. I thought it would be runnable once I got back up the initial hill, but it was mud pit after mud pit, and I would have two steps of running in between mud pits to carefully walk through. It was really frustrating. I ended up texting to my parents and Scott that it was about 1.7 miles of mud (from the uphill, and the plateau) before I got to some gravel that was more easily runnable. Woohoo for gravel! This was a nice, short downhill slope (D) before we flattened out and switched back to dirt and more mud pits.
This was the E area, although it did feel more runnable than the plateau because there were longer stretches between muddy sections.
Eventually, we saw the river and came out from the trail into a parking lot and then jogged over onto the trail that parallels the river for a while. This trail that I thought of as “River Road” (starting around point F) is just mowed grass and is between a sharp bluff drop with opening where people would be down at the river fishing, and in some cases we were running *underneath* fishing lines from the parking spots down to the river! There were a few people who would be walking back and forth from cars to the river, but in general they were all very courteous and there was no obstruction of the trail. Despite the mowed grass aspect of the trail, this stretch physically and psychologically felt easier because there were no mud pits for 90% of it. Near the end there were a few muddy areas right about the point we hopped back over into the road to connect up a gravel road for a short spurt.
This year, the race actually put a bonus aid station out here. I didn’t partake, but they had a tent up with two volunteers who were cheerful and kind to passing runners, and it looked like they had giant things of gatorade or water, bottled water, and some sugared soda. They probably had other stuff, but that’s just what I saw when passing.
After that short gravel road bit, we turned back onto a dirt trail that led us to the river. Not the big river we had been running next to, but the place where the Columbia River overflowed the trail and we had to cross it. This is what the race director meant by practicing our backstroke.
You can see a video in this tweet of how deep and far across you had to get in this river crossing (around point G, but hopefully in future years this isn’t a point of interest on the map!!)
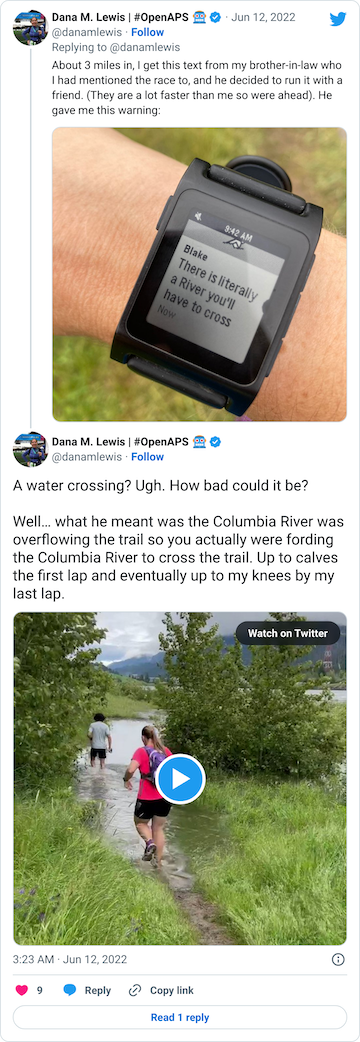
Coming out of the river, my feet were like blocks of ice. I cheered up at the thought that I had finished the wet feet portion of the course and I’d dry off before I looped back around and hit the muddy hill and plateau again. But, sadly, just around the next curve, came a mud POND. Not a pit, a pond.
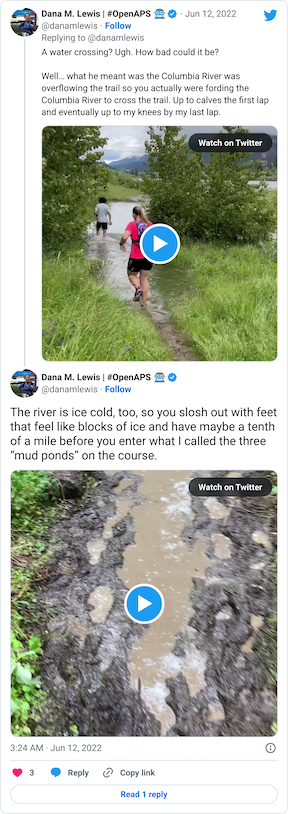
Again, ankle deep water and mud, not just once but in three different ponds all within 30 seconds or so of each other. It was really frustrating, and obviously you can’t run through them, so it slowed you down.
Then finally after the river crossing and the mud ponds, we hooked a right into a nice, forest trail that we spent about a mile and a half in (point H). It had a few muddy spots like you would normally expect to get muddy on a trail, but it wasn’t ankle deep or water filled or anything else. It was a nice relief!
Then we turned out of the forest and crossed a road and headed up one more (tiny, but it felt annoying despite how small it looks on the elevation profile) hill (point I), ran down the other side of that slope, stepped across another mud pond onto a pleasingly gravel path, and took the gravel path about .3 miles back all the way to complete the first full lap.
Phew.
I actually made pretty good time the first loop despite not knowing about all the mud or river crossing challenges. I was pleased with my time which was on track with my plan. Scott took my pack about .1 miles before I entered the start/finish area and brought it back to me refilled as I exited the start/finish area.
Lap 2:
The second lap was pretty similar. The Hill (A) felt remarkably harder after having experienced the first loop. I did try to run more of the downhill (B) as I recognized I’d make up some time from the walking climb as well as knowing I couldn’t run up the plateau or some of the mud pits along the plateau (C) as well as I had expected. I also decided running in the mud pits didn’t work, and went with the safer approach of stepping through them and then running 2 steps in between. I was a little slower this time, but still a reasonable pace for my goals.
The rest of the loop was roughly the same as the first, the mud was obnoxious, the river crossing freezing, the mud obnoxious again, and relief at running through the forest.
Scott met me at the end of the river road and biked along the short gravel section with me and went ahead so he could park his bike and take video of my second river crossing, which is the video above. I was thrilled to have video of that, because the static pictures of the river crossing didn’t feel like it did the depth and breadth of the water justice!
At the end of lap 2, Scott grabbed my pack again at the end of the loop and said he’d figured out where to meet me to give it back to me after the hill…if I wanted that. Yes, please! The bottom of the hill where you hairpin turn to go back up the plateau is the 1 mile marker point, so that means I ran the first mile of the third lap without my pack, and not having the weight of my full pack (almost 3L of water and lots of snacks and supplies: more on that pack below) was really helpful for my third time up the hill. He met me as planned at the bottom of the downhill (B) and I took my pack back which made a much nicer start to lap 3.
Lap 3:
Lap 3 for some reason I came out of the river crossing and the mud ponds feeling like I got extra mud in my right shoe. It felt gritty around the right side of my right food, and I was worried about having been running for so many hours with soaked feet. I decided to stop at a bench in the forest section and swap for dry socks. In retrospect, I wish I had stopped somewhere else, because I got swarmed by these moth/gnat/mosquito things that looked gross (dozens on my leg within a minute of sitting there) that I couldn’t brush off effectively while I was trying to remove my gaiters, untie my shoes, take my shoes off, peel my socks and bandaids and lambs wool off, put lubrication back on my toes, put more lambs wool on my toes, put the socks and shoes back on, and re-do my gaiters. Sadly, it took me 6 minutes despite me moving as fast as I could to do all of those things (this was a high/weirdly designed bench in a shack that looked like a bus stop in the middle of the woods, so it wasn’t the best way to sit, but I thought it was better than sitting on the ground).
(The bugs didn’t hurt me at the time, but two days later my dozens of bites all over my leg are red and swollen, though thankfully they only itch when they have something chafing against them.)
Anyway, I stood up and took off again and was frustrated knowing that it had taken 6 minutes and basically eaten the margin of time I had against my previous 50k time. I saw Scott about a quarter of a mile later, and I saw him right as I realized I had also somewhere lost my baggie of electrolyte pills. Argh! I didn’t have back up for those (although I had given Scott backups of everything else), so that spiked my stress levels as I was due for some electrolytes and wasn’t sure how I’d do with 3 or so more hours without them.
I gave Scott my pack and tasked him with checking my brother-in-law’s setup to see if he had spare electrolytes, while he was refilling my pack to give me in lap 4.
Lap 4:
I was pretty grumpy given the sock timing and the electrolyte mishap as I headed into lap 4. The hill still sucked, but I told myself “only one more hill after this!” and that thought cheered me up.
Scott had found two electrolyte options from my brother-in-law and brought those to me at the end of mile 1 (again, bottom of B slope) with my pack. He found two chewable and two swallow pills, so I had options for electrolytes. I chewed the first electrolyte tab as I headed up the plateau, and again talked myself through the mud pits with “only one more time through the mud pits after this!”.
I also tried overall to bounce back from the last of mile 4 where I let myself get frustrated, and try to take more advantage of the runnable parts of the course. I ran downhill (B) more than the previous laps, mostly ignoring the audio cues of my 30:60 intervals and probably running more like 45:30 or so. Similarly, the downhill gravel after the mud pits (D) I ran most of without paying attention to the audio run cues.
Scott this time also met me at the start of the river road section, and I gave him my pack again and asked him to take some things out that he had put in. He put in a bag with two pairs of replacement socks instead of just one pair of socks, and also put in an extra beef stick even though I didn’t ask for it. I asked him to remove it, and he did, but explained he had put it in just in case he didn’t find the electrolytes because it had 375g of sodium. (Sodium is primarily the electrolyte I am sensitive to and care most about). So this was actually a smart thing, although because I haven’t practiced eating larger amounts of protein and experienced enzyme dosing for it on the run, I would be pretty nervous about eating it in a race, so that made me a bit unnecessarily grumpy. Overall though, it was great to see him extra times on the course at this point, and I don’t know if he noticed how grumpy I was, but if he did he ignored it and I cheered up again knowing I only had “one more” of everything after this lap!
The other thing that helped was he biked my pack down the road to just before the river crossing, so I ran the river road section like I did lap 3 and 4 on the hill, without a pack. This gave me more energy and I found myself adding 5-10 seconds to the start of my run intervals to extend them.
The 4th river crossing was no less obnoxious and cold, but this time it and the mud ponds didn’t seem to embed grit inside my shoes, so I knew I would finish with the same pair of socks and not need another change to finish the race.
Lap 5:
I was so glad I was only running the 50k so that I only had 5 laps to do!
For the last lap, I was determined to finish strong. I thought I had a chance of making up a tiny bit of the sock change time that I had lost. I walked up the hill, but again ran more than my scheduled intervals downhill, grabbed my bag from Scott, picked my way across the mud pits for the final time (woohoo!), ran the downhill and ran a little long and more efficiently on the single track to the river road.
Scott took my pack again at the river road, and I swapped my intervals to be 30:45, since I was already running closer to that and I knew I only had 3.5 or so miles to go. I took my pack back at the end of river road and did my last-ever ice cold river crossing and mud pond extravaganza. After I left the last mud pond and turned into the forest, I switched my intervals to 30:30. I managed to keep my 30:30 intervals and stayed pretty quick – my last mile and a half was the fastest of the entire race!
I came into the finish line strong, as I had hoped to finish. Woohoo!
Overall strengths and positives from the race
Overall, running-wise I performed fairly well. I had a strong first lap and decent second lap, and I got more efficient on the laps as I went, staying focused and taking advantage of the more runnable parts of the course. I finished strong, with 30:45 intervals for over a mile and 30:30 intervals for over a mile to the finish.
Also, I didn’t quit after experiencing the river crossing and the mud ponds and the mud pits of the first lap. This wasn’t an “A” race for me or my first time at the distance, so it would’ve been really easy to quit. I probably didn’t in part because we did pay to spend the night before and drove all that way, and I didn’t want to have “wasted” Scott’s time by quitting, when I was very capable of continuing and wasn’t injured. But I’m proud of mostly the way I handled the challenges of the course, and for how I readjusted from the mental low and frustration after realizing how long my sock change took in lap 3. I’m also pleased that I didn’t get injured, given the terrain (mud, river crossing, and uneven grass to run on for most of the course). I’m also pleased and amazed I didn’t hurt my feet, cause major blisters, or have anything really happen to them after hours of wet, muddy, never-drying-off feet.
The huge positive was my fueling, electrolytes, and blood glucose management.
I started taking my electrolyte pills that have 200+mg of sodium at about 45 minutes into the race, on schedule. My snack choices also have 100-150mg of sodium, which allowed me to not take electrolyte pills as often as I would otherwise need to (or on a hotter day with more sweat – it was a damp, mid-60s day but I didn’t sweat as much as I usually do). But even with losing my electrolytes, I used two chewable 100mg sodium electrolytes instead and otherwise ended up with sufficient electrolytes. Even with ideal electrolyte supplementation, I’m very sensitive to sodium losses and am a salty sweater, and I have a distinct feeling when my electrolytes are insufficient, so not having that feeling during after the race was a big positive for me.
So was my fueling overall. The race started at 9am, and I woke up at 6am to eat my usual pre-race breakfast (a handful of pecans, plus my enzyme supplementation) so that it would both digest effectively and also be done hitting my blood sugar by the time the race started. My BGs were flat 120s or 130s when I started, which is how I like them. I took my first snack about an hour and 10 minutes into the race, which is about 15g carb (10g fat, 2g protein) of chili cheese flavored Fritos. For this, I didn’t dose any insulin as I was in range, and I took one lipase-only enzyme (which covers about 8g of fat for me) and one multi-enzyme (that covers about 6g of fat and probably over a dozen grams of protein). My second snack was an hour later, when I had a gluten free salted caramel Honey Stinger stroopwaffle (21g carb, 6 fat, 1 protein). For the stroopwaffle I ended up only taking a lipase-only pill to cover the fat, even though there’s 1g of protein. For me, I seem to be ok (or have no symptoms) from 2-3g of uncovered fat and 1-2g of uncovered protein. Anything more than that I like to dose enzymes for, although it depends on the situation. Throughout the day, I always did 1 lipase-only and 1 multi-enzyme for the Fritos, and 1 lipase-only for the stroopwaffle, and that seemed to work fine for me. I think I did a 0.3u (less than a third of the total insulin I would normally need) bolus for my stroopwaffle because I was around 150 mg/dL at the time, having risen following my un-covered Frito snack, and I thought I would need a tiny bit of insulin. This was perfect, and I came back down and flattened out. An hour and 20 minutes after that, I did another round of Fritos. An hour or so after that, a second stroopwaffle – but this time I didn’t dose any insulin for it as my BG was on a downward slope. An hour later, more Fritos. A little bit after that, I did my one single sugar-only correction (an 8g carb Airhead mini) as I was still sliding down toward 90 mg/dL, and while that’s nowhere near low, I thought my Fritos might hit a little late and I wanted to be sure I didn’t experience the feeling of a low. This was during the latter half of loop 4 when I was starting to increase my intensity, so I also knew I’d likely burn a little more glucose and it would balance out – and it did! I did one last round of Fritos during lap 5.
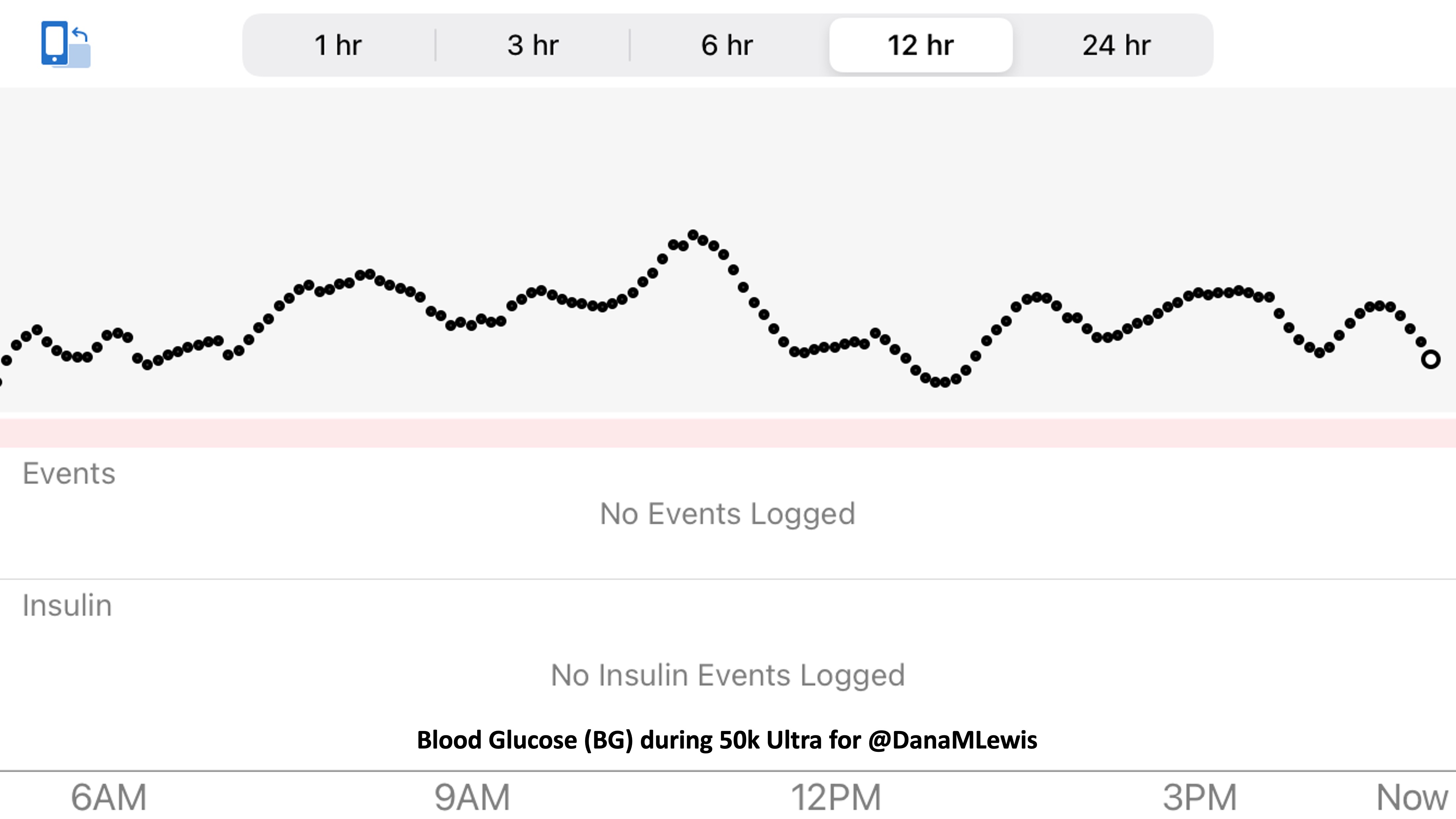
This all worked perfectly. I had 100% time in range between 90 and 150 mg/dL, even with 102g of “real food” carbs (15g x 4 servings of Fritos, 21g x 2 waffles), and one 8g Airhead mini, so in total I had 110g grams of carbs across ~7+ hours. This perfectly matched my needs with my run/walk moderate efforts.
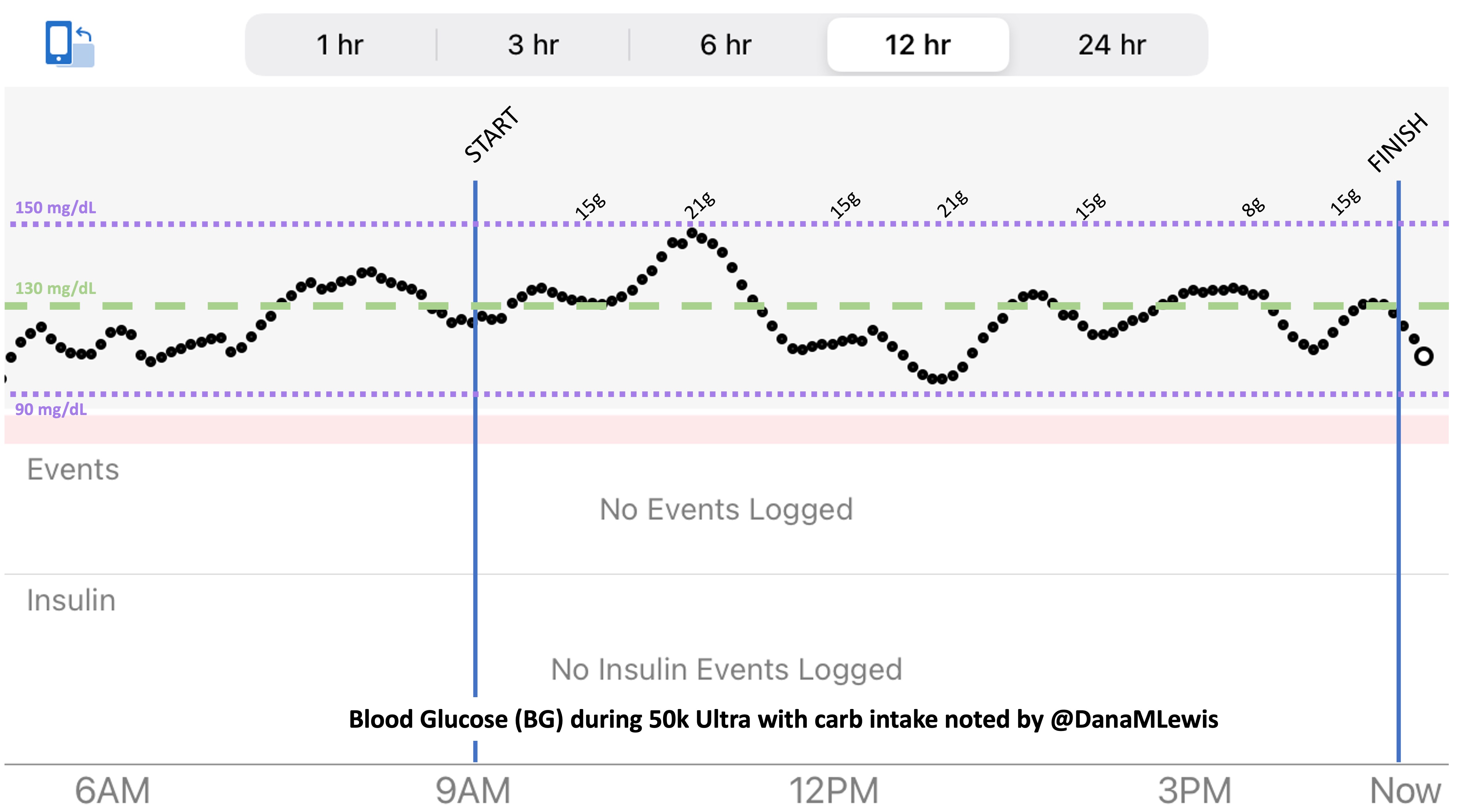
I also nailed the enzymes, as during the race I didn’t have any GI-related symptoms and after the race and the next day (which is the ultimate verdict for me with EPI), no symptoms.
So it seems like my practice and testing with low carbs, Fritos, and waffles worked out well! I had a few other snacks in my pack (yogurt-covered pretzels, peanut butter pretzel nuggets), but I never thought of wanting them or wanting something different. I did plan to try to do 2 snacks per hour, but I ended up doing about 1 per hour. I probably could have tolerated more, but I wasn’t hungry, my BGs were great, and so although it wasn’t quite according to my original plan I think this was ideal for me and my effort level on race day.
The final thing I think went well was deciding on the fly after loop 2 to have Scott take my pack until after the hill (so I ran the up/downhill mile without it), and then for additional stretches along river road in laps 4 and 5. I had my pocket of my shorts packed with dozens of Airheads and mints, so I was fine in terms of blood sugar management and definitely didn’t need things for a mile at a time. I’m usually concerned about staying hydrated and having water whenever I want to sip, plus for swallowing electrolytes and enzyme pills to go with my snacks, but I think on this course with the number of points Scott could meet me (after B, at F all through G, and from I to the finish), I could have gotten away with not having my pack the whole time; having WAY less water in the pack (I definitely didn’t need to haul 3L the whole time, that was for when I might not see Scott every 2-3 laps) and only one of each snack at a time.
Areas for improvement from my race
I trained primarily on gravel or paved trails and roads, but despite the “easy” elevation profile and terrain, this was essentially my first trail ultra. I coped really well with the terrain, but the cognitive burden of all the challenges (Mud pits! River crossing! Mud ponds!) added up. I’d probably do a little more trail running and hills (although I did some) in the final weeks before the race to help condition my brain a little more.
I’ll also continue to practice fueling so I can eat more regularly than every hour to an hour and a half, even though this was the most I’ve ever eaten during a run, I did well with the quantities, and my enzyme and BG management were also A+. But I didn’t eat as much as I planned for, and I think that might’ve helped with the cognitive fatigue, too, by at least 5-10%.
I also now have the experience of a “stop” during a race, in this case to swap my socks. I’ve only run one ultra and never stopped before to do gear changes, so that experience probably was sufficient prep for future stops, although I do want to be mentally stronger/less frustrated by unanticipated problem solving stops.
Specific to this course, as mentioned above, I could’ve gotten away with less supplies – food and water – in my pack. I actually ran a Ragnar relay race with a group of fellow T1s a few years back where I finished my run segment and…no one was there to meet me. They went for Starbucks and took too long to get there, so I had to stand in the finishing chute waiting for 10-15 minutes until someone showed up to start the next run leg. Oh, and that happened in two of the three legs I ran that day. Ooof. Standing there tired, hot, with nothing to eat or drink, likely added to my already life-with-type-1-diabetes-driven-experiences of always carrying more than enough stuff. But I could’ve gotten away very comfortably with carrying 1L of water and one set of each type of snacks at a time, given that Scott could meet me at 1 mile (end of B), start (F) and end of river road (before G), and at the finish, so I would never have been more than 2-2.5 miles without a refill, and honestly he could’ve gotten to every spot on the trail barring the river crossing bit to meet me if I was really in need of something. Less weight would’ve made it easier to push a little harder along the way. Basically, I carried gear like I was running a solo 30 mile effort at a time, which was safe but not necessary given the course. If I re-ran this race, I’d feel a lot more comfortable with minimal supplies.
Surprises from my race
I crossed the finish line, stopped to get my medal, then was waiting for my brother-in-law to finish another lap (he ran the 100k: 62 miles) before Scott and I left. I sat down for 30 minutes and then walked to the car, but despite sitting for a while, I was not as stiff and sore as I expected. And getting home after a 3.5 hour car ride…again I was shocked at how minimally stiff I was walking into the house. The next morning? More surprises at how little stiff and sore I was. By day 3, I felt like I had run a normal week the week prior. So in general, I think this is reinforcement that I trained really well for the distance and my long runs up to 50k and the short to medium next day runs also likely helped. I physically recovered well, which is again part training but also probably better fueling during the race, and of course now digesting everything that I ate during and after the race with enzyme supplementation for EPI!
However, the interesting (almost negative, but mostly interesting) thing for me has been what I perceived to be adrenal-type fatigue or stress hormone fatigue. I think it’s because I was unused to focusing on challenging trail conditions for so many hours, compared to running the same length of hours on “easy” paved or gravel trails. I actually didn’t listen to an audiobook, music, or podcast for about half of the race, because I was so stimulated by the course itself. What I feel is adrenal fatigue isn’t just being physically or mentally tired but something different that I haven’t experienced before. I’m listening to my body and resting a lot, and I waited until day 4 to do my first easy, slow run with much longer walk intervals (30s run, 90s walk instead of my usual 30:60). Day 1 and 2 had a lot of fatigue and I didn’t feel like doing much, Day 3 had notable improvement on fatigue and my legs and body physically felt back to normal for me. Day 4 I ran slowly, Day 5 I stuck with walking and felt more fatigue but no physical issues, Day 6 again I chose to walk because I didn’t feel like my energy had fully returned. I’ll probably stick with easy, longer walk interval runs for the next week or two with fewer days running until I feel like my fatigue is gone.
General thoughts about ultramarathon training and effective ultra race preparation
I think preparation makes a difference in ultramarathon running. Or maybe that’s just my personality? But a lot of my goal for this race was to learn what I could about the course and the race setup, imagine and plan for the experience I wanted, plan for problem solving (blisters, fuel, enzymes, BGs, etc), and be ready and able to adapt while being aware that I’d likely be tired and mentally fatigued. Generally, any preparation I could do in terms of deciding and making plans, preparing supplies, etc would be beneficial.
Some of the preparation included making lists in the weeks prior about the supplies I’d need in my pack, what Scott should have to refill my pack, what I’d need the night and morning before since we would not be at home, and after-race supplies for the 3.5h drive home.
From the lists, the week before the race I began grouping things. I had my running pack filled and ready to go. I packed my race outfit in a gallon bag, a full set of backup clothes in another gallon bag and labeled them, along with a separate post-run outfit and flip flops for the drive home. I also included a washcloth for wiping sweat or mud off after the run, and I certainly ended up needing that! I packed an extra pair of shoes and about 4 extra pairs of socks. I also had separate baggies with bandaids of different sizes, pre-cut strips of kinesio tape for my leg and smaller patches for blisters, extra squirrel nut butter sticks for anti-chafing purposes, as well as extra lambs wool (that I lay across the top of my toes to prevent socks from rubbing when they get wet from sweat or…river crossings, plus I can use it for padding between my toes or other blister-developing spots). I had sunscreen, bug spray, sungless, rain hat, and my sunny-weather running visor that wicks away sweat. I had low BG carbs for me to put in my pockets, a backup bag for Scott to refill, and a backup to the backup. The same for my fuel stash: my backpack was packed, I packed a small baggie for Scott as well as a larger bag with 5-7 of everything I thought I might want, and also an emergency backup baggie of enzymes.
*The only thing I didn’t have was a backup baggie of electrolyte pills. Next time, I’ll add this to my list and treat them like enzymes to make sure I have a separate backup stash.
I even made a list and gave it to Scott that mapped out where key things were for during and after the race. I don’t think he had to use it, because he was only digging through the snack bag for waffles and Fritos, but I did that so I didn’t have to remember where I had put my extra socks or my spare bandaids, etc. He basically had a map of what was in each larger bag. All of this was to reduce the decision and communication because I knew I’d have decision fatigue.
This also went for post-race planning. I told Scott to encourage me to change clothes, and it was worth the energy to change so I didn’t sit in cold, wet clothes for the long drive home. I pre-made a gluten free ham and cheese quesadilla (take two tortillas, fill with shredded cheese and slices of ham, microwave, cut into quarters, stick in baggies, mark with fat/protein/carb counts, and refrigerate) so we could warm that up in the car (this is what I use) so I had something to eat on the way home that wasn’t more Fritos or waffles. I didn’t end up wanting it, but I also brought a can of beef stew with carrots and potatoes, that I generally like as a post-race or post-run meal, and a plastic container and a spoon so I could warm up the stew if I wanted it. Again, all of this pre-planned and put on the list weeks prior to the race so I didn’t forget things like the container or the spoon.
The other thing I think about a lot is practicing everything I want to do for a race during a training run. People talk about eating the same foods, wearing the same clothes, etc. I think for those of us with type 1 diabetes (or celiac, EPI, or anything else), it’s even more important. With T1D, it’s so helpful to have the experience adjusting to changing BG levels and knowing what to do when you’re dropping or low and having a snack, vs in range and having a fueling snack, or high and having a fueling snack. I had 100% TIR during this run, but I didn’t have that during all of my training runs. Sometimes I’d plateau around 180 mg/dL and be over-cautious and not bring my BGs down effectively; other times I’d overshoot and cause a drop that required extra carbs to prevent or minimize a low. Lots of practice went into making this 100% TIR day happen, and some of it was probably a bit of luck mixed in with all the practice!
But generally, practice makes it a lot easier to know what to do on the fly during a race when you’re tired, stressed, and maybe crossing an icy cold river that wasn’t supposed to be part of your course experience. All that helps you make the best possible decisions in the weirdest of situations. That’s the best you can hope for with ultrarunning!














Recent Comments