I observe a number of people who seem to think it’s inevitable that once someone gets sick, the rest of the house is going to get sick with 100% certainty.
Nope.
First of all, household transmission rates are less than 100% for all of these conditions, even if you didn’t take any precautions or make any behavior changes.
Secondly, with knowledge about how these things spread and some mitigation measures, you can reduce this a lot – and in some cases to nearly zero.
I will caveat: that of course depending on the situation some of these precautions may not make sense or be possible. For example, if you have kids, your exposures may be different. We don’t have kids in our house, so we are dealing with adult to adult possible transmission. That being said, some of these things may still be worth doing to some degree, to cut down the risk of exposure and/or to limit the viral dose you are exposed to, even in a situation that is less straightforward like a parent taking care of sick kids.
PS – if you’re reading this in January 2025 and don’t read the rest, make sure you’ve gotten your flu shot (yes, it helps) for the 2024-2025 flu season. No, it’s not too late. If you’re >65, you should also check about the RSV vaccine (which like the flu shot is a seasonal vaccine). It’s not too late and given the current high rates of RSV and flu (and soon to be uptick in COVID), they can help prevent getting or limit the severity if you do get exposed.
Our experience preventing the spread of RSV and the common cold
I can speak with recent, practical experience on this.
Twice.
First, let’s talk about RSV.
Before Thanksgiving, Scott and I were exposed to a nibling (aka a niece or nephew – of which we have 10 plus several honorary ones!) who had what we thought was a lingering cough from a cold from a few weeks ago. Because I am avoiding infection, I wore a mask inside and did not get up close to the nibling, so as a result of all of this likely had minimal exposure. Scott did not mask and had spent a lot more time with this nibling hanging all over him and coughing near or on him. Within 48 hours, he started to get symptoms of something.
We activated our plan for household transmission avoidance. Well, with a rolling start: Scott recognized by Thanksgiving evening that he was starting to feel unwell and had a tiny bit of coughing. I thought I could hear something in his chest differently, in addition to the occasional cough, so I went into full precaution mode while Scott did a partial precaution mode. This meant we set up air purifiers by each of our beds, and a fan pointed in my direction so all air was blowing away from me. I also wore a mask to go to sleep in. (This was super annoying and I don’t like doing this, especially because I usually take a shower and go to bed with wet hair. Wearing an n95 with head straps on wet hair plus having a fan and purifier blowing on me is chilly and unfun.) I would’ve preferred Scott to mask, too, or go to the guest bedroom to sleep, but it was late in the evening; he wasn’t convinced he was really sick; and I was too exhausted to argue about it on top of the fact that we were leaving on a trip the next morning. So he did not mask that night.
The next morning, though, he was definitely sick. He tested negative for COVID, and the nibling and everyone else from that house had been testing for COVID and negative, so we were fairly confident based on serial testing that this was not COVID. At the time, the thought was this was a common cold.
Since we were planning to mask in indoor spaces, anyway, including in the airport and on the plane, we felt comfortable going on our trip as planned, because we would be unlikely to infect anyone else. (This includes no indoor dining: we don’t take off our masks and eat inside.)
Because Scott realized he was sick, he masked from that point forward (with a non-valved N95). We both masked in the car, in the airport, on the plane, and again when we arrived while driving in the rental car. Then a challenge: we needed to eat dinner (we got takeout), and we were sharing a hotel room overnight. We switched from a hotel room with a king bed to a room with two queen beds, which would give us some more space overnight. But we took turns eating dinner unmasked in the hotel room (it was too cold to be outside) with the far-UVC lights on and the purifiers around each of us when we ate. While we ate, the other person was masked. (And I went first, so there was no unmasked air from Scott while I was eating and he went second). We also took turns showering, again with me going first and him not having been in the bathroom unmasked until after I had gone in. Other than that, we stayed masked in the hotel room including overnight, again with purifiers between us and the far-UVC lights running.
(This hotel did not have windows that opened to outside, but if there had been windows I would’ve eaten in front of the open window and we would’ve likely kept it cracked open and the heat turned up, to improve the room’s ventilation).
The next day, we had more of a drive, and again we masked. We also slightly rolled down the windows in the backseat to improve ventilation. Scott sometimes took his mask off for comfort stretches, because he was driving, but put it back on fully and sealed it before coughing. I kept my mask on without ceasing. We did a 4.5 hour drive this way.
Luckily, once we arrived at our destination, there was a spare bedroom, so that became Scott’s headquarters. He stayed masked in the living room/shared areas. He sat downwind outside and masked up when coughing if anyone was outside. We left the sliding door to the outside cracked open, in order to keep the air in the common areas well-ventilated. This worked, because we were able to keep CO2 levels (a proxy for ventilation) down below 700 ppm most of the time.
Because we had separate bedrooms, we did not mask while sleeping the rest of the week, because we each had our own rooms (and own airflow). I did keep a purifier running in my room all week, but that’s my habit regardless because I’m so allergic to dust.
And guess what? It all worked. We masked again on the drive back to the airport and in the airport and on the plane and again once we got home.
I never got RSV. The four other adults we spent time with and shared a house with….also did not get RSV. So we are pretty confident that the transmission chain stopped completely at Scott.
In summary, what worked:
- Masking in shared spaces, and two-way masking when it wasn’t possible to ventilate
- When we had to sleep in the same room, two-way masking even for sleeping overnight
- Scott masking in shared spaces that were well ventilated, and often left the room to go cough even when masked (or coughing outside). This often meant he masked, but the rest of us did not mask inside the whole time.
- Generally keeping distance. Droplets were managed by the N95 mask, and we were ventilating to reduce aerosol transmission risk, but still keeping physical distance to further reduce the risk.
RSV is *very* transmissible especially with aerosols, and Scott was coughing a lot all day and night. (At one point, his Sleep Cycle app was estimating 18 coughs per hour). It took a long time for that to get down to normal, so he continued to sleep in our guest room when we got back and we continued to ventilate well even when we gradually reduced masking once he stopped coughing. It took about 10 or so days for all of his biometrics to normalize, and about 14 days for his cough to completely go away. It probably was closer to three weeks before he finally felt all recovered.
So with that timing in mind, you know what happens 4 weeks after Thanksgiving? Christmas/other end of year holiday gatherings.
We had plans to see 8 kids and 8 adults (plus us) for Christmas. And at Christmas, it seemed like everyone had a cold already. So again, I went in and mostly masked except for when I was in front of an open window and the room was well ventilated, without anyone coughing actively in the room. (If anyone was in the room with me and coughing, especially the kids, I would mask even with the window open).
I did not get the cold that 8-10 (out of 16) people eventually got.
But…Scott did. And this time, he was mostly masked, but he still spent more time up close with kids who were coughing quite a bit. And this is where some of the dynamics of knowing WHAT people have is helpful. You can’t always know, but you can sometimes use the symptoms to figure out what people have.
For example, based on symptoms of the nibling who passed on germs to Scott around Thanksgiving, and Scott’s symptoms (instant, incredible chest cough but no runny nose, sore throat, fever, or aches) we had ultimately guessed that Scott had RSV. We then knew that the biggest risk was either droplets from coughing (especially because the volume of coughing), which could be reduced drastically by masking, or aerosols, which again would be helped by his masking and also ventilation, and in closed spaces, two-way masking (me masking).
For the Christmas germs, everyone seemed to have mild symptoms with congestion, runny noses, some coughs. But no fevers or aches and it seemed less severe. Given our recent experience with RSV, we narrowed it down to likely being a cold (rhinovirus), given again everyone testing repeatedly negative for COVID.
Given that, we knew the risk was going to be highest for us from droplets and fomites. So we again masked in shared spaces; Scott went to sleep in the guest bedroom as soon as he started getting symptoms; and we both did a lot of hand washing. Scott washed his hands before touching any of my things and regularly wiped down the kitchen. I tried not to go in the kitchen much (our main overlapping shared space), but also wash my hands after any time that I did. He didn’t have much of a cough and it was more controlled, so he would hold his cough until he could cover it with a mask or be in the room by himself. We also did our usual running of purifiers and opened windows and ran fans to increase ventilation to keep CO2 low.
And again? It worked. I did not get the cold, either from any of the ~8+ folks who did across the holiday period, or from Scott. Scott’s vitals all returned to normal at the five day mark, although we continued to mask in the car through day 7, to be more cautious (due to my personal situation).
So, infection is not inevitable, even in small houses and apartments.
Here’s what we’ve taken away from these experiences with more aerosol-based (RSV) transmission diseases and more droplet and fomite-based (cold) experiences:
- Two-way N95 masking works. Mask in the car, run the fan, keep the windows cracked, run purifiers at home, and ventilate spaces, but you still want two-way masking when something is aerosolized and you’re in the same spaces. This can prevent transmission.
- Keep distance when someone is coughing and sneezing (and if they have a cough or sneeze type illness, you want 6 foot distance even when they’re not actively coughing or sneezing, because they make droplets just from breathing and talking). The person who’s coughing and sneezing should mask, even inside, unless they are in their own room in private (and it’s not a shared room).Keep your air ventilated (if you haven’t, read my post about ventilation and using a Co2 monitor)Depending on the illness, to fully protect yourself you’ll need to commit to wearing a mask at all times indoors to protect yourself if the person who is sick is not masking. (Eg, Scott got a cold while mostly masked around heavily coughing niblings, but not throughout the whole house the whole day). With adults, the adults who are sick should definitely mask if they’re in shared spaces with other adults. (It’s harder with kids, and it should be a conversation depending on the age of the kids about them masking in shared spaces, such as if they want to play with Uncle Scott, or help them understand that someone may not want to play up close if they’re sick and coughing and not willing to mask. That’s fine, but that’s a choice they can make when kids are old enough to understand.)
- Have the infected person sleep in a different space (on the couch or in another room if you have a spare bedroom). If you have to share a room, both should mask.
- Use cleaning wipes to wipe down shared surfaces (e.g. fridge handles, microwave, counters, bathroom surfaces like the flush on the toilet or sink faucet, etc) and wash your hands after using these shared spaces every time. Fomites can last longer than you’d expect.
- Use metrics from your wearable devices (eg Apple Watch or Oura ring or similar) to track when your temperature, respiratory rate, heart rate, cough rate, etc. return to normal. That tied with symptom elimination can help you determine how long you’re likely most infectious for. The general estimates of contagiousness for each condition generally seem to be right (e.g., two weeks for an adult with RSV and 5-7 days for a cold) in our recent experiences. I would continue precautions for at least those minimum time frames, if you can.
- Yes, there’s a cost to these precautions, in terms of human contact. There was no hugging or hand holding or kissing or any touch contact during these time periods. I felt pretty lonely, especially because it was me we were trying to protect (because I am at high risk for bad outcomes due to immunosuppression right now), and I’m sure Scott also felt lonely and isolated. That part sucked, but we at least knew it was a fixed period of time, which helped.
What we’d do differently next time
 This basically has been our plan for if either of us were to get COVID-19 (or the flu), and it’s good to know this plan works for a variety of conditions including RSV and the common cold. The main thing we would do differently in the future is that Scott should have masked the very first night he had symptoms of RSV, and he has decided that he’ll be masking any time he’s in the same room as someone who’s been coughing, as that’s considerably less annoying than being sick. (He really did not like the experience of having RSV.) I obviously did not get it from that first night when he first had the most minor symptoms of RSV, but that was probably the period of highest risk of transmission of either week, given the subsequent precautions we took after that.
This basically has been our plan for if either of us were to get COVID-19 (or the flu), and it’s good to know this plan works for a variety of conditions including RSV and the common cold. The main thing we would do differently in the future is that Scott should have masked the very first night he had symptoms of RSV, and he has decided that he’ll be masking any time he’s in the same room as someone who’s been coughing, as that’s considerably less annoying than being sick. (He really did not like the experience of having RSV.) I obviously did not get it from that first night when he first had the most minor symptoms of RSV, but that was probably the period of highest risk of transmission of either week, given the subsequent precautions we took after that.
Combined, everything we did worked, and we’ll do it again when we need to in the future, which should not be very often. We went five full years without either of us getting any type of infection (yay), and hopefully that continues from here on out. We’ll also continue to get regular COVID-19 boosters; annual flu shots; and other annual shots if/when they become available (e.g. when we reach the age, getting the RSV vaccine).
—
Remember, if you’re reading this in January 2025, RSV and flu levels are very high in the US right now, with COVID-19 expected to pick up again soon. It’s not too late to get your boosters and given the rates of respiratory illness, consider situational masking even if you don’t typically mask.
 It sounds nice. Hopeful. Productive. It implies the lemons are gently handed to you. They’re probably clean, ripe, and maybe sitting in a cute little basket. Like life’s just giving you a quirky unexpected opportunity.
It sounds nice. Hopeful. Productive. It implies the lemons are gently handed to you. They’re probably clean, ripe, and maybe sitting in a cute little basket. Like life’s just giving you a quirky unexpected opportunity. And sometimes people do. That’s valid. Sometimes I’ve done that.
And sometimes people do. That’s valid. Sometimes I’ve done that. Forget the default script. There’s no “right” way to respond.
Forget the default script. There’s no “right” way to respond. This has become a long post, with no clear messages or resolutions, which in of itself is an example of these types of situations. Hard, uncertain, messy, no clear ending or answer or what next. But these types of situations happen a lot, more than you know.
This has become a long post, with no clear messages or resolutions, which in of itself is an example of these types of situations. Hard, uncertain, messy, no clear ending or answer or what next. But these types of situations happen a lot, more than you know. As an example for how I like to disseminate my articles personally, every time a journal article is published and I have access to it, I updated
As an example for how I like to disseminate my articles personally, every time a journal article is published and I have access to it, I updated 
 How do you have people take the EPI/PEI-SS? You can pull this link up (
How do you have people take the EPI/PEI-SS? You can pull this link up ( This came to mind because he went on a work trip, and I stuck things in the dishwasher for 2 days, and jokingly texted him to “come home and do the dishes that the raccoon left”. He came home well after dinner that night, and the next day texted when he opened the dishwasher for the first time that he “opened the raccoon cage for the first time”. (LOL).
This came to mind because he went on a work trip, and I stuck things in the dishwasher for 2 days, and jokingly texted him to “come home and do the dishes that the raccoon left”. He came home well after dinner that night, and the next day texted when he opened the dishwasher for the first time that he “opened the raccoon cage for the first time”. (LOL).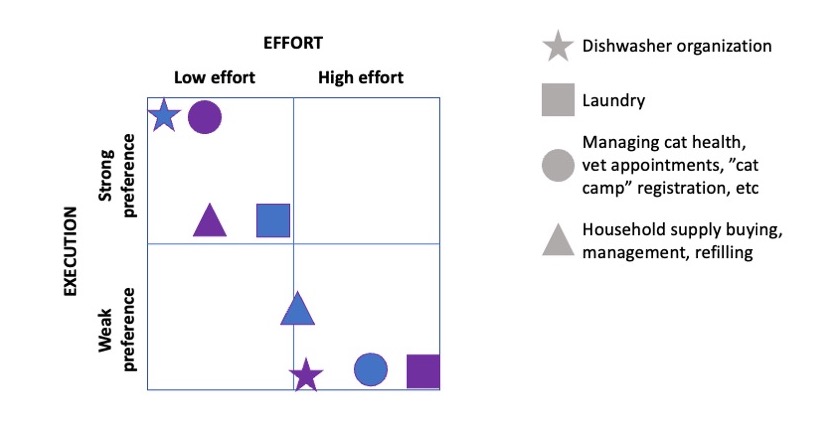

Recent Comments