Life for a Child is an international non-profit organization that supports children with diabetes by providing insulin, test strips, and essential diabetes care to over 60,000 children in low-income countries who would otherwise have little to no access to treatment.
Without access to supplies and skilled medical care, children with type 1 diabetes (T1D) often die quickly, and with only intermittent access may die within a few years of diagnosis. In some countries, limited amounts and types of older insulins may be provided by the health systems. In these ‘luckier’ countries, test strips are still not usually provided. Without regular blood glucose testing, children may survive into early adulthood, yet still experience early mortality due to long-term complications such as blindness, kidney failure, or amputations.
Life for a Child (LFAC) offers a lifeline, extending life expectancy and improving the quality of life for children at a remarkably low cost. Life for a Child also does incredibly critical work in improving care delivery infrastructures in each of these countries that they support. They work directly with local healthcare providers to co-develop critical education materials for young people living with diabetes. Further, they provide a support network to local healthcare providers and some governments. This is all to help improve sustainability of access to services, medications, and support for people with diabetes in the long run.
Scott and I have been supporting Life for a Child as our charity of choice for many years. As we wrote in our analysis here in 2017:
“Life for a Child seems like a fairly effective charity, spending about $200-$300/yr for each person they serve (thanks in part to in-kind donations from pharmaceutical firms). If we assume that providing insulin and other diabetes supplies to one individual (and hopefully keeping them alive) for 40 years is approximately the equivalent of preventing a death from malaria, that would mean that Life for a Child might be about half as effective as AMF, which is quite good compared to the far lower effectiveness of most charities, especially those that work in first world countries.”
We used some of GiveWell’s analyses to assess effective giving, especially comparing options like GiveDirectly or more specific charity options like AMF:
“For example, the Against Malaria Foundation, the recommended charity with the most transparent and straightforward impact on people’s lives, can buy and distribute an insecticide-treated bed net for about $5. Distributing about 600-1000 such nets results in one child living who otherwise would have died, and prevents dozens of cases of malaria. As such, donating 10% of a typical American household’s income to AMF will save the lives of 1-2 African kids *every year*.”
(Note: In addition to donations, I also have supported Life for a Child with my time at both the US level, serving on the US-based Life for a Child US board, as well as the US representative on the international steering committee for Life for a Child.)
However, in 2025, Life for a Child faces an immediate and unexpected $300,000 funding shortfall, due to a previously committed donor no longer being able to provide this donation. This funding was for test strips, which will reduce the number of strips provided per child from three to two test strips per day.
Further, Life for a Child has additional funding needs to continue expanding to support more children who are otherwise unsupported and going without critical supplies. (The room for funding is several orders of magnitude above this year’s funding gap.)
In order to assess the need for how we (in a general sense, speaking of all of us) fill this funding gap and understanding if this is still a cost-effective way to support people with diabetes, we wanted to revisit our analysis for how cost-effective Life For a Child is.
For background, I asked Graham Ogle, head of LFAC, for some numbers. These include:
- Life for A Child currently supports 60,000 children in 2025
- The original expansion plan is a goal to support 100,000 children or more by 2030
- Estimates for how much is spent per child is about $150 USD (slightly less than what Scott and I had estimated in 2017), or $160 USD if you incorporate indirect costs.
We used these numbers below to estimate the cost-effectiveness of Life for a Child’s interventions.
Estimating Life For A Child’s Cost per Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY)
The Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY) is the most commonly used metric in global health to capture both the years of life lost (YLL) due to premature death and the years lived with disability (YLD) due to a health condition, such as type 1 diabetes.
The goal of Life for a Child’s work is to reduce both of these by providing insulin and glucose monitoring as well as improved care necessary for improved health outcomes.
- Life for a Child support reduces Years of Life Lost (YLL)
To estimate YLL reduction, we calculate the difference between the expected age at death for a child with T1D who receives no care versus a child receiving LFAC support:
- Without Life for a Child :
- In the worst-case scenario, children with T1D may die within 1-2 years due to lack of insulin, meaning an early death by age 10 instead of the typical life expectancy of 60 years in some of these countries. . This results in 50 YLLs (60 – 10 = 50).
- In countries where insulin is available but costly and/or glucose monitoring is not affordable and readily available, children may survive into their late 20s or 30s, but still experience significant complications, reducing life expectancy. In this scenario (minimal access to insulin, glucose monitoring, etc), we make a rough assumption that children with diabetes may survive into their mid to late 30s, therefore 25 YLLs is a reasonable estimate (60 – 35 = 25).
- With Life for a Child :
- Life for a Child’s program significantly improves both short-term and long-term survival. We assume that children supported by Life for a Child have the potential to live to an average life expectancy of 50-60 years (instead of dying prematurely due to untreated T1D), even when considering that LFAC only supports children into early adulthood (e.g. 25-30 years of age).
If we assume the average life expectancy for children newly diagnosed with T1D increases from 15-35 years to 50-60 years with standard Life for a Child support, that gives a savings of 25-35 YLLs (DALYs) per child, accounting for most of the uncertainty in our lifespan estimates above.
- Years Lived with Disability (YLD) Reduction
T1D also causes significant disability when people with T1D don’t have access to insulin and/or sufficient glucose monitoring and monitoring for early signs of complications, especially due to complications like blindness, kidney failure, and amputations. Each of these conditions brings about substantial life impairment.
- Without Life for a Child:
- Children with poorly supported T1D face a high likelihood of severe complications as they age. We estimate the disability weight (DW) for this scenario at 0.20, reflecting significant disability as a result of some of those complications.
- With Life for a Child:
- Access to insulin and glucose monitoring and healthcare monitoring drastically reduces the risk of complications. We estimate a DW of 0.05, which represents a much lower level of disability, especially in terms of future complications.
With such DWs, the reduction in YLD before premature death (20%-5%=15% over 5-30 years = 1-4 DALYs), and the 5% reduction in the YLL benefit (5% * 25-35 = 1-2 DALYs) partially cancel out, and don’t change the end result much. The net gain of 1-2 DALYs due to YLD reduction is smaller than the uncertainty range on the YLL benefit.
So for purposes of cost-effectiveness calculations, we’ll ignore YLD in the rest of this post and continue using the 25-35 DALYs per child figure.
- Total DALYs and Cost per DALY
For this section, we’ll assume the total impact of Life for a Child’s intervention per child from the calculations above is 25-35 DALYs.
Life for a Child’s cost per child in 2025 is approximately $150 per year (or $160 including indirect costs), and if we estimate that most children receive treatment for about 15 years, meaning the total cost per child is roughly $1,500–$2,250 over that period (or $1,600-$2,400 total with indirect costs).
Thus, the cost per DALY for Life for a Child can be estimated as:
(Cost per child) / (DALYs saved per child)
Here are a variety of estimates for varying cost levels using the lower bound of 25 DALYs saved per child supported:
- With $1,500 per lifetime per child ($150/year for 10 years) and 25 DALYs saved, that estimates $60 per DALY ($64 with indirect costs)
- With $2,250 per lifetime per child ($150/year for 15 years) and 25 DALYs saved, that estimates $90 per DALY ($96 with indirect costs)
- With slightly higher costs to assume the cost will rise over time of $175/year for 15 years, this is a higher estimated $2,625 per lifetime per child and 25 DALYs saved, estimating $105 per DALY.
- With slightly higher costs to assume the cost will rise over time of $175/year for 20 years, this is a higher estimated $3,500 per lifetime per child and 25 DALYs saved, estimating $140 per DALY.
This places Life for a Child’s cost per DALY in the range of $60–$90, for conservative estimates a remarkably cost-effective intervention, and even the higher estimates of $105-$140 assuming an increase in costs and increase in years of support compares favorably to the most effective global health programs, including those recommended by GiveWell.
How did we come to this conclusion?
- GiveWell estimates cash transfers through GiveDirectly result in $1000/DALY, based on welfare gains rather than direct health outcomes (so apples and oranges), but even apples to oranges we can estimate Life for a Child is more cost-effective by at least single digit (eg 1-9x) factors than cash giving elsewhere.
- We know GiveWell’s top charities are around $50-$100/DALY. Given we were estimating $60-$140 with a wide swathe of estimates, we can see that Life for a Child aligns with some of GiveWell’s top charities in terms of cost per DALY and thus “compares favorably” in our analysis.
Why You Should Donate to Life for a Child
The point of this post was for Scott and I to reassess our statement that we have been making since ~2017 or so, which is the fact that Life for a Child is a remarkably cost-effective charity overall, and likely one of the most cost-effective charities to support people living with diabetes around the world who otherwise won’t have access (or regular access) to insulin and blood glucose testing.
Life for a Child has a DALY cost in the range of $60-$140 (reflecting current versus future cost increases), depending on which input variables you use, which makes it one of the best uses of global health funding available today.
Because of this reassessment, we also hope if you’ve read this far that you, too, will consider making a life-saving and life-changing donation for people with diabetes by donating to Life for a Child.
If you’re feeling overwhelmed with world events and want to make a tangible difference in people’s lives in a measurable way, consider donating to Life for a Child.
If you want to support people with diabetes in the most cost-effective way, so that your donation dollars make the biggest impact? Donate to Life for a Child.
Your donation saves – and changes – lives.
 (Thank you).
(Thank you).
PS – feel free to reach out to me (Dana@OpenAPS.org) and/or Scott (Scott@OpenAPS.org) if you want to chat through any of the estimates or numbers in more detail and how we consider donations.
 I encourage you to think about scaling yourself and identifying a task or series of tasks where you can get in the habit of leveraging these tools to do so. Like most things, the first time or two might take a little more time. But once you figure out what tasks or projects are suited for this, the time savings escalate. Just like learning how to use any new software, tool, or approach. A little bit of invested time up front will likely save you a lot of time in the future.
I encourage you to think about scaling yourself and identifying a task or series of tasks where you can get in the habit of leveraging these tools to do so. Like most things, the first time or two might take a little more time. But once you figure out what tasks or projects are suited for this, the time savings escalate. Just like learning how to use any new software, tool, or approach. A little bit of invested time up front will likely save you a lot of time in the future. If you have been prescribed pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT), aka enzymes for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI or PEI), you may be wondering how long it will take before you start to feel better or it starts to work. This is a common question, and the answer depends on several factors, including the dosage, meal composition, and how well your body uses the enzymes. Some improvements can be seen within a single meal, while other benefits take longer to manifest. It also depends on whether you have EPI, or if you have EPI in concert with other types of gastrointestinal conditions, because some of your symptoms may be coming from other conditions.
If you have been prescribed pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT), aka enzymes for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI or PEI), you may be wondering how long it will take before you start to feel better or it starts to work. This is a common question, and the answer depends on several factors, including the dosage, meal composition, and how well your body uses the enzymes. Some improvements can be seen within a single meal, while other benefits take longer to manifest. It also depends on whether you have EPI, or if you have EPI in concert with other types of gastrointestinal conditions, because some of your symptoms may be coming from other conditions.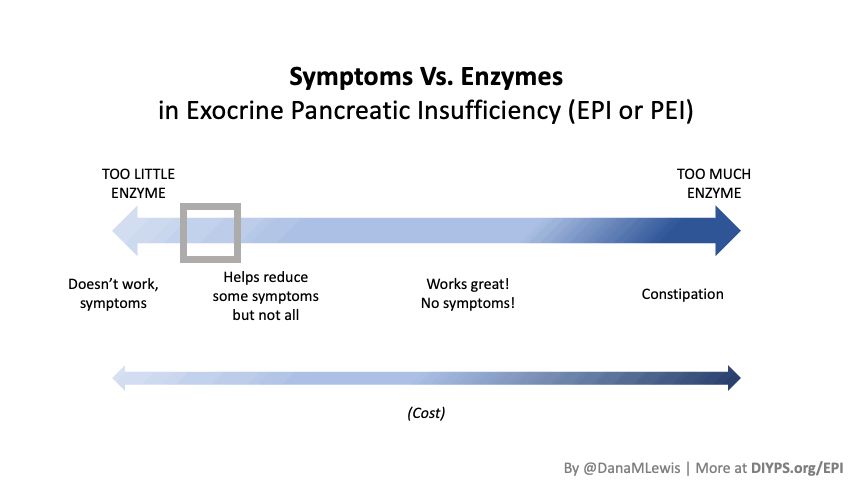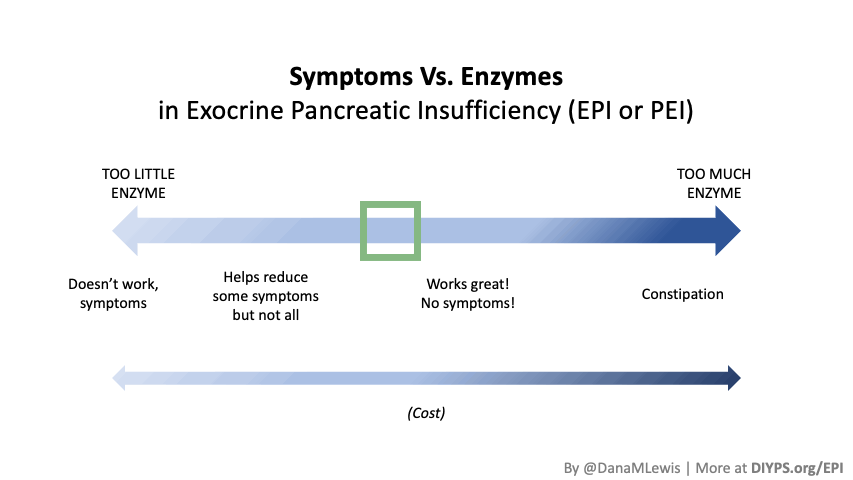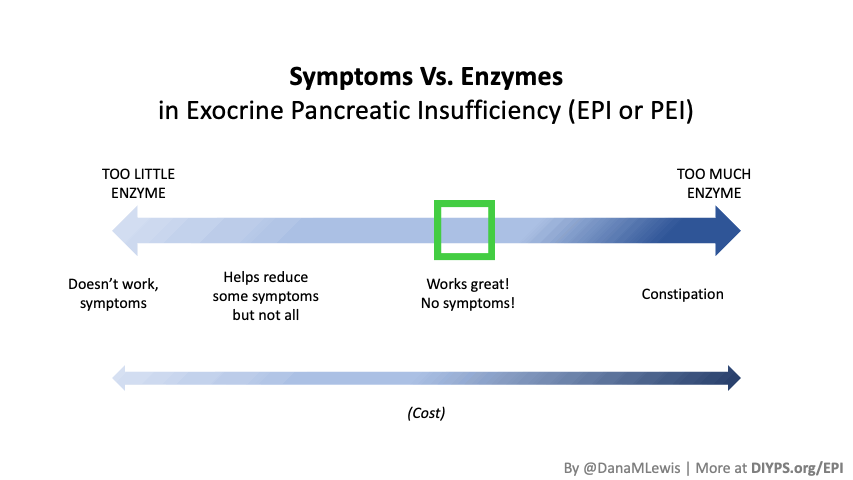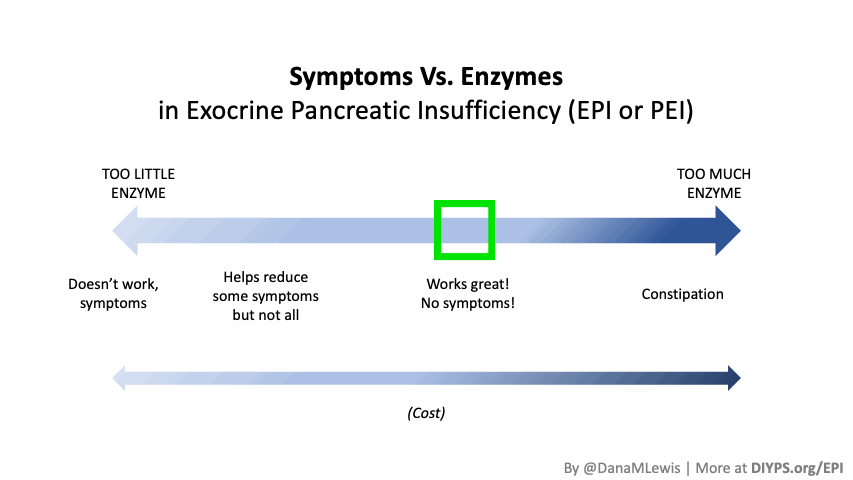
 TL;DR: Instead of arbitrarily lowering or increasing fat or fiber in the diet, measure and estimate what you are consuming first. If you have EPI,
TL;DR: Instead of arbitrarily lowering or increasing fat or fiber in the diet, measure and estimate what you are consuming first. If you have EPI,  It occurred to me that maybe I could tweak it somehow and make the bullets of the list represent food items. I wasn’t sure how, so I asked the LLM if it was possible. Because I’ve done my other ‘design’ work in PowerPoint, I went there and quickly dropped some shapes and lines to simulate the icon, then tested exporting – yes, you can export as SVG! I spent a few more minutes tweaking versions of it and exporting it. It turns out, yes, you can export as SVG, but then the way I designed it wasn’t really suited for SVG use. When I had dropped the SVG into XCode, it didn’t show up. I asked the LLM again and it suggested trying PNG format. I exported the icon from powerpoint as PNG, dropped it into XCode, and it worked!
It occurred to me that maybe I could tweak it somehow and make the bullets of the list represent food items. I wasn’t sure how, so I asked the LLM if it was possible. Because I’ve done my other ‘design’ work in PowerPoint, I went there and quickly dropped some shapes and lines to simulate the icon, then tested exporting – yes, you can export as SVG! I spent a few more minutes tweaking versions of it and exporting it. It turns out, yes, you can export as SVG, but then the way I designed it wasn’t really suited for SVG use. When I had dropped the SVG into XCode, it didn’t show up. I asked the LLM again and it suggested trying PNG format. I exported the icon from powerpoint as PNG, dropped it into XCode, and it worked! If you can shift your mindset from fear and avoidance to curiosity and experimentation, you might discover new skills, solve problems you once thought were impossible, and open up entirely new opportunities.
If you can shift your mindset from fear and avoidance to curiosity and experimentation, you might discover new skills, solve problems you once thought were impossible, and open up entirely new opportunities.
 TLDR: Instead of asking “Which model is best?”, a better question might be:
TLDR: Instead of asking “Which model is best?”, a better question might be: AI can be useful for reducing clinician workload and improving documentation efficiency. But like any tool, its impact depends on how it’s implemented, how transparent the process is, and whether there are safeguards to address errors when they occur.
AI can be useful for reducing clinician workload and improving documentation efficiency. But like any tool, its impact depends on how it’s implemented, how transparent the process is, and whether there are safeguards to address errors when they occur. This basically has been our plan for if either of us were to get COVID-19 (or the flu), and it’s good to know this plan works for a variety of conditions including RSV and the common cold. The main thing we would do differently in the future is that Scott should have masked the very first night he had symptoms of RSV, and he has decided that he’ll be masking any time he’s in the same room as someone who’s been coughing, as that’s considerably less annoying than being sick. (He really did not like the experience of having RSV.) I obviously did not get it from that first night when he first had the most minor symptoms of RSV, but that was probably the period of highest risk of transmission of either week, given the subsequent precautions we took after that.
This basically has been our plan for if either of us were to get COVID-19 (or the flu), and it’s good to know this plan works for a variety of conditions including RSV and the common cold. The main thing we would do differently in the future is that Scott should have masked the very first night he had symptoms of RSV, and he has decided that he’ll be masking any time he’s in the same room as someone who’s been coughing, as that’s considerably less annoying than being sick. (He really did not like the experience of having RSV.) I obviously did not get it from that first night when he first had the most minor symptoms of RSV, but that was probably the period of highest risk of transmission of either week, given the subsequent precautions we took after that.
Recent Comments