—
#DIYPS + @danamlewis = as good as a bionic pancreas! Reduced avg. BG & time spent <60mg/dl. Details: http://bit.ly/1qF6qRp @scottleibrand
—
Recently, diaTribe published a summary of results presented by Dr. Ed Damiano at #ATTD2014 showing how their bionic pancreas closed loop artificial pancreas system (APS) improved average glucose levels and halved time spent <60 mg/dl in patients with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), compared to when those same patients were not wearing the system. The numbers are impressive: mean glucose was reduced from 159 mg/dl to 133 mg/dl in the Beacon Hill study (n=20 adults, 5 days data per patient, for a total of 100 bionic pancreas days). If that were sustained over the long term and converted to an A1c value, that would represent a 0.9% improvement, from 7.1% to 6.2%. As diaTribe points out, “Those results are unheard of for any diabetes drug or device.”
Given those results, we wanted to see how the bionic pancreas results compared to the results for #DIYPS, and the results were equally impressive: 90-day eAG was better than in any of the study control groups prior to using the system (before #DIYPS =146 mg/dl) and eAG was further reduced to better than any of the bionic pancreas treatment groups (after #DIYPS = 128 mg/dl) after utilizing #DIYPS. Time spent <60 mg/dl was already lower than for any of the bionic pancreas treatment groups (before #DIYPS = 1.2%), but was reduced still further to 0.9% with #DIYPS.
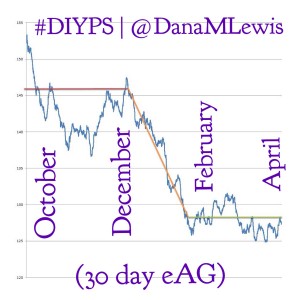
(Note that for #DIYPS, n=1 at the moment. These results are specific to a single highly motivated individual, who was already doing everything possible to manage T1D.)
The pre-DIYPS control condition included wearing and using both a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) and an insulin pump. It is not clear from the diaTribe article whether the subjects in the bionic pancreas study under their “Usual Care” or “Supervised Camp Care” control conditions included the use of such technology, or whether they were using the more common methods of fingerstick meters and multiple daily injections (MDI) of insulin. If “Usual Care” included patients on MDI, much of the benefit attributed to the bionic pancreas could be attainable using CGM+pump therapy as well. The #DIYPS data, however, shows significant improvements even compared to CGM+pump in the control condition.
While n=1 (vs. n=20 and n=32 in the two bionic pancreas studies), the #DIYPS data shows the effects of much longer term usage of the #DIYPS system. The total time using the system (90-100 days) was equivalent between our data and the Beacon Hill study. Also, because #DIYPS has been in use for 100 days now, we have now seen the results in actual A1c values, not just eAG-calculated Projected A1c. The improvement from pre-DIYPS A1c to the first post-DIYPS A1c data point is consistent with the improvement shown by the calculated eAG results. (Note that we plan to validate with additional data from A1c testing to show the actual improvement in A1c attributable to #DIYPS, and hopefully validating the sustainability of using the system).
Differences between the bionic pancreas & #DIYPS
Part of what makes the bionic pancreas so promising is that it is able to dose glucagon (through a second pump) to correct low or falling BGs. Because #DIYPS uses only an existing FDA-approved CGM, relies on the patient to dose their own insulin through an FDA-approved insulin pump, and is not using glucagon, #DIYPS might not be expected to be able to prevent hypoglycemia as well as the bionic pancreas. However, our data show that #DIYPS’ predictive alarms and proactive correction suggestions allow a patient to prevent hypoglycemia (BGs <60 mg/dl) even better than the bionic pancreas can do. (#DIYPS also suggests, when possible, using temporary basal rates, which often reduces the extra carbohydrates that have to be consumed to prevent or correct a low BG). Less-motivated patients using #DIYPS may not be able to prevent low BGs quite as effectively, but this is still an important demonstration that such improvements in control are possible before new glucagon pump technology is available on the market in the future.
Differences between bionic pancreas, artificial pancreas systems (APS), and #DIYPS
And finally, and most importantly as a distinction of the difference from the bionic pancreas, #DIYPS does not automatically dose insulin. It is solely an alerting system (with predictive alerting and real-time calculation abilities), which relies on the user to both validate any suggested actions, and to actually dose any insulin, reduce insulin, or consume any carbohydrates required to manage their BGs. This means #DIYPS is not an artificial pancreas system (APS), and does not provide the ability for you to “forget about diabetes” that is such a powerful promise of true APS systems like the bionic pancreas. Yet it does reduce the overall cognitive load of diabetes (and provides additional security mechanisms such as alerting loved ones if you don’t respond to alarms over time). And, #DIYPS shows that better software and alerting can result in dramatic improvements in blood glucose levels, even without automatic dosing of insulin.
What’s next for #DIYPS
As you can tell, we are excited about the promise of #DIYPS for helping people with diabetes (PWD) manage their disease. But, as mentioned above, all of this is currently being done in our spare time, with no funding or institutional support. We, and a small group of like-minded individuals and non-profits scattered across the Internet, have decided that #WeAreNotWaiting for research labs and medical device companies to develop a full APS system and get it approved by the FDA (which is still probably 5 years away). Instead, we are doing what we can to make progress now.
But the next step is critical: we need to make this technology available to the people whose quality of life – and possibly even whose lives – depend on it. (This is why we originally set out to build #DIYPS – to help people wake up to overnight CGM alerts who sleep through the one-size-fit-all alarms coming from the device). Recently we received an email from someone in Europe whose MD tells her that her severe nocturnal hypoglycemia is life threatening, and sent her on a mission to find a system that can wake her up from a severe low and contact a loved one if she doesn’t respond. In order to help people like her, we need to begin working with researchers and doctors, and hopefully even get funding to develop #DIYPS into a scalable system that can help any PWD manage their diabetes better.
If you are someone (or know anyone) who can help with any aspect of that effort, please reach out to us on Twitter or directly by email. Otherwise, please stay tuned for more updates.
–Dana Lewis and Scott Leibrand



Recent Comments